
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 89835 by john santu last updated on 19/Apr/20
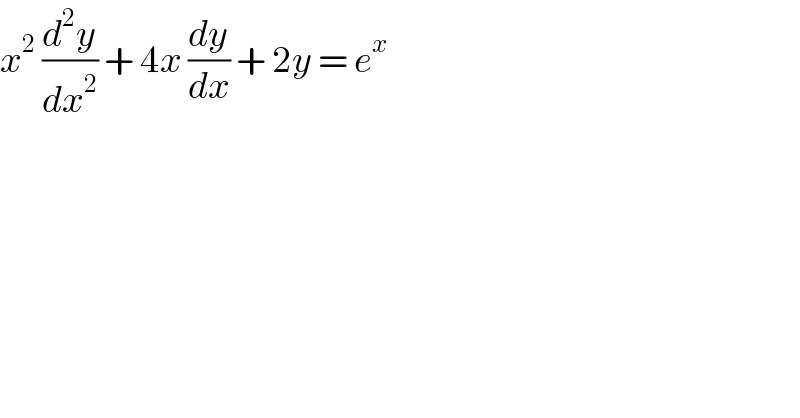
$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\:\mathrm{4}{x}\:\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\:+\:\mathrm{2}{y}\:=\:{e}^{{x}} \\ $$
Answered by Joel578 last updated on 19/Apr/20
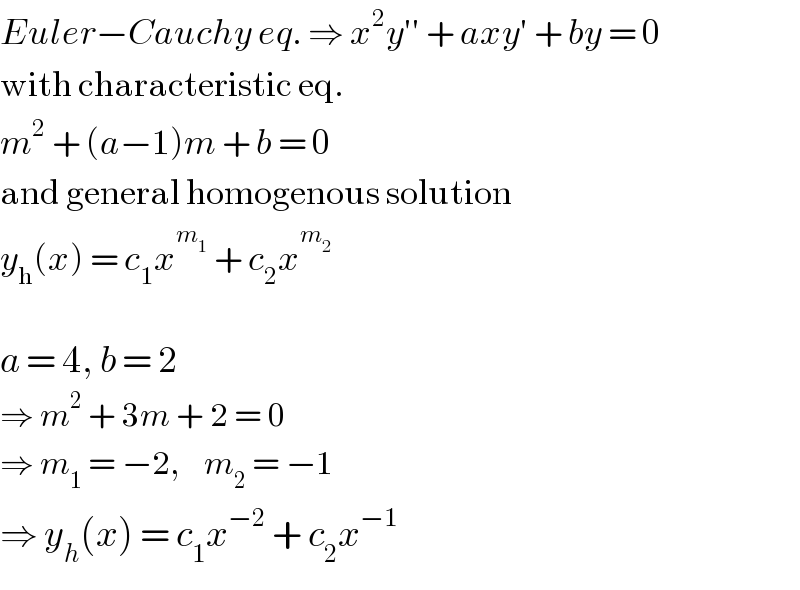
$${Euler}−{Cauchy}\:{eq}.\:\Rightarrow\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}''\:+\:{axy}'\:+\:{by}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{characteristic}\:\mathrm{eq}. \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\:\left({a}−\mathrm{1}\right){m}\:+\:{b}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{general}\:\mathrm{homogenous}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$${y}_{\mathrm{h}} \left({x}\right)\:=\:{c}_{\mathrm{1}} {x}^{{m}_{\mathrm{1}} } \:+\:{c}_{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{{m}_{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${a}\:=\:\mathrm{4},\:{b}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{m}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\:\mathrm{3}{m}\:+\:\mathrm{2}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{m}_{\mathrm{1}} \:=\:−\mathrm{2},\:\:\:\:{m}_{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\:{y}_{{h}} \left({x}\right)\:=\:{c}_{\mathrm{1}} {x}^{−\mathrm{2}} \:+\:{c}_{\mathrm{2}} {x}^{−\mathrm{1}} \\ $$
Answered by TANMAY PANACEA. last updated on 19/Apr/20
![x=e^t (dx/dt)=e^t (dy/dt)×(dt/dx)=(dy/dx) (dy/dt)×(1/e^t )=(dy/dx) x(dy/dx)=(dy/dt) (d/dx)((dy/dx))→(d/dt)((1/e^t )(dy/dt)).(dt/dx) =[(1/e^t ).(d^2 y/dt^2 )+(dy/dt).(1/e^t ).(−1)]×(1/e^t ) (d^2 y/dx^2 )=((1/e^t ))^2 .(d^2 y/dt^2 )−((1/e^t ))^2 .(dy/dt) x^2 (d^2 y/dx^2 )=(d^2 y/dt^2 )−(dy/dt) so x^2 .(d^2 y/dx^2 )+4x(dy/dx)+2y=e^x (d^2 y/dt^2 )−(dy/dt)+4(dy/dt)+2y=e^e^t (θ^2 +3θ+2)y=e^e^t θ=(d/dt) (θ+1)(θ+2)=0 C.F Ae^(−t) +Be^(−2t) →(A/x)+(B/x^2 ) y=(e^x /((θ+1)(θ+2)))=[(1/(θ+1))−(1/(θ+2))]e^x =(e^x /(θ+1))−(e^x /(θ+2)) =(e^x /(θ−(−1)))−(e^x /(θ−(−2))) =x^(−1) ∫x^(1−1) e^x dx−x^(−2) ∫x^(2−1) e^x dx =x^(−1) .e^x −x^(−2) ∫xe^x =(e^x /x)−(1/x^2 )[xe^x −1.e^x ] =(e^x /x)−(e^x /x)+(e^x /x^2 ) y=(A/x)+(B/x^2 )+(e^x /x^2 )](Q89883.png)
$${x}={e}^{{t}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}={e}^{{t}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}×\frac{{dt}}{{dx}}=\frac{{dy}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{{t}} }=\frac{{dy}}{{dx}} \\ $$$${x}\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}=\frac{{dy}}{{dt}} \\ $$$$\frac{{d}}{{dx}}\left(\frac{{dy}}{{dx}}\right)\rightarrow\frac{{d}}{{dt}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{{t}} }\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}\right).\frac{{dt}}{{dx}} \\ $$$$=\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{{t}} }.\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{dy}}{{dt}}.\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{{t}} }.\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)\right]×\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{{t}} } \\ $$$$\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{{t}} }\right)^{\mathrm{2}} .\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{e}^{{t}} }\right)^{\mathrm{2}} .\frac{{dy}}{{dt}} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} \frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\frac{{d}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}}{{dt}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{{dy}}{{dt}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{so}} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{x}}^{\mathrm{2}} .\frac{\boldsymbol{{d}}^{\mathrm{2}} \boldsymbol{{y}}}{\boldsymbol{{dx}}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\mathrm{4}\boldsymbol{{x}}\frac{\boldsymbol{{dy}}}{\boldsymbol{{dx}}}+\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{y}}=\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{x}}} \\ $$$$\frac{\boldsymbol{{d}}^{\mathrm{2}} \boldsymbol{{y}}}{\boldsymbol{{dt}}^{\mathrm{2}} }−\frac{\boldsymbol{{dy}}}{\boldsymbol{{dt}}}+\mathrm{4}\frac{\boldsymbol{{dy}}}{\boldsymbol{{dt}}}+\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{{y}}=\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{e}}^{\boldsymbol{{t}}} } \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left(\theta^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{3}\theta+\mathrm{2}\right){y}={e}^{{e}^{{t}} } \:\:\:\theta=\frac{{d}}{{dt}} \\ $$$$\left(\theta+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\theta+\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{C}}.{F} \\ $$$${Ae}^{−{t}} +{Be}^{−\mathrm{2}{t}} \rightarrow\frac{{A}}{{x}}+\frac{{B}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${y}=\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{\left(\theta+\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\theta+\mathrm{2}\right)}=\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\theta+\mathrm{1}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\theta+\mathrm{2}}\right]{e}^{{x}} \\ $$$$=\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{\theta+\mathrm{1}}−\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{\theta+\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$=\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{\theta−\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)}−\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{\theta−\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)} \\ $$$$={x}^{−\mathrm{1}} \int{x}^{\mathrm{1}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} {dx}−{x}^{−\mathrm{2}} \int{x}^{\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{{x}} {dx} \\ $$$$={x}^{−\mathrm{1}} .{e}^{{x}} −{x}^{−\mathrm{2}} \int{xe}^{{x}} \\ $$$$=\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\left[{xe}^{{x}} −\mathrm{1}.{e}^{{x}} \right] \\ $$$$=\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}}−\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}}+\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{y}}=\frac{\boldsymbol{{A}}}{{x}}+\frac{\boldsymbol{{B}}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{e}^{{x}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$
