
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 91321 by M±th+et+s last updated on 29/Apr/20
![1)find eigen values and corresponding eigen vector of the matrix A= [((cos(θ)),(−sin(θ))),((sin(θ)),( cos(θ))) ] 2)solve 6y^2 dx−x(y+2x^2 )dy=0](Q91321.png)
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 30/Apr/20
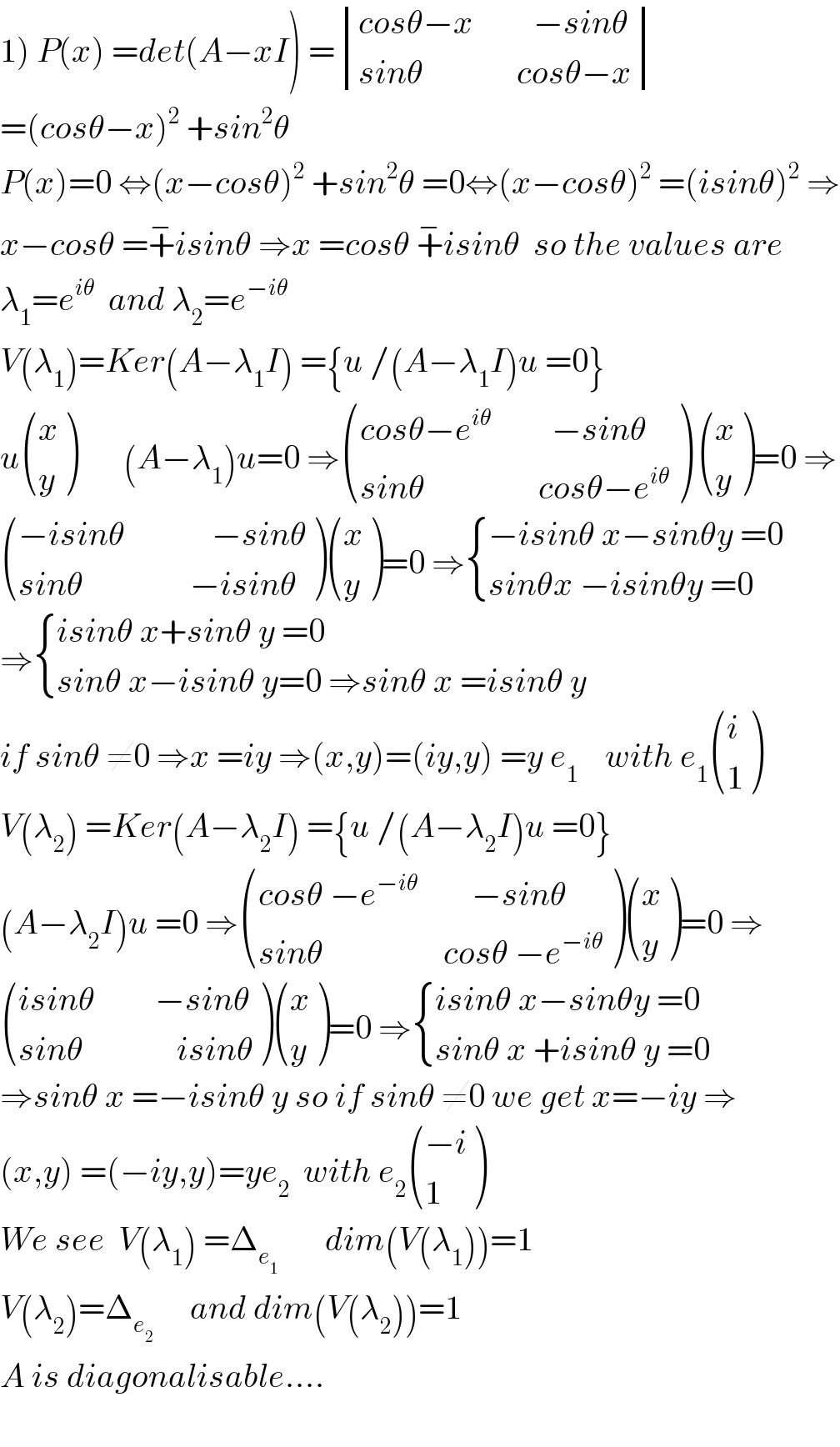
Commented by M±th+et+s last updated on 30/Apr/20
Commented by turbo msup by abdo last updated on 30/Apr/20
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 91321 by M±th+et+s last updated on 29/Apr/20 | ||
![1)find eigen values and corresponding eigen vector of the matrix A= [((cos(θ)),(−sin(θ))),((sin(θ)),( cos(θ))) ] 2)solve 6y^2 dx−x(y+2x^2 )dy=0](Q91321.png) | ||
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 30/Apr/20 | ||
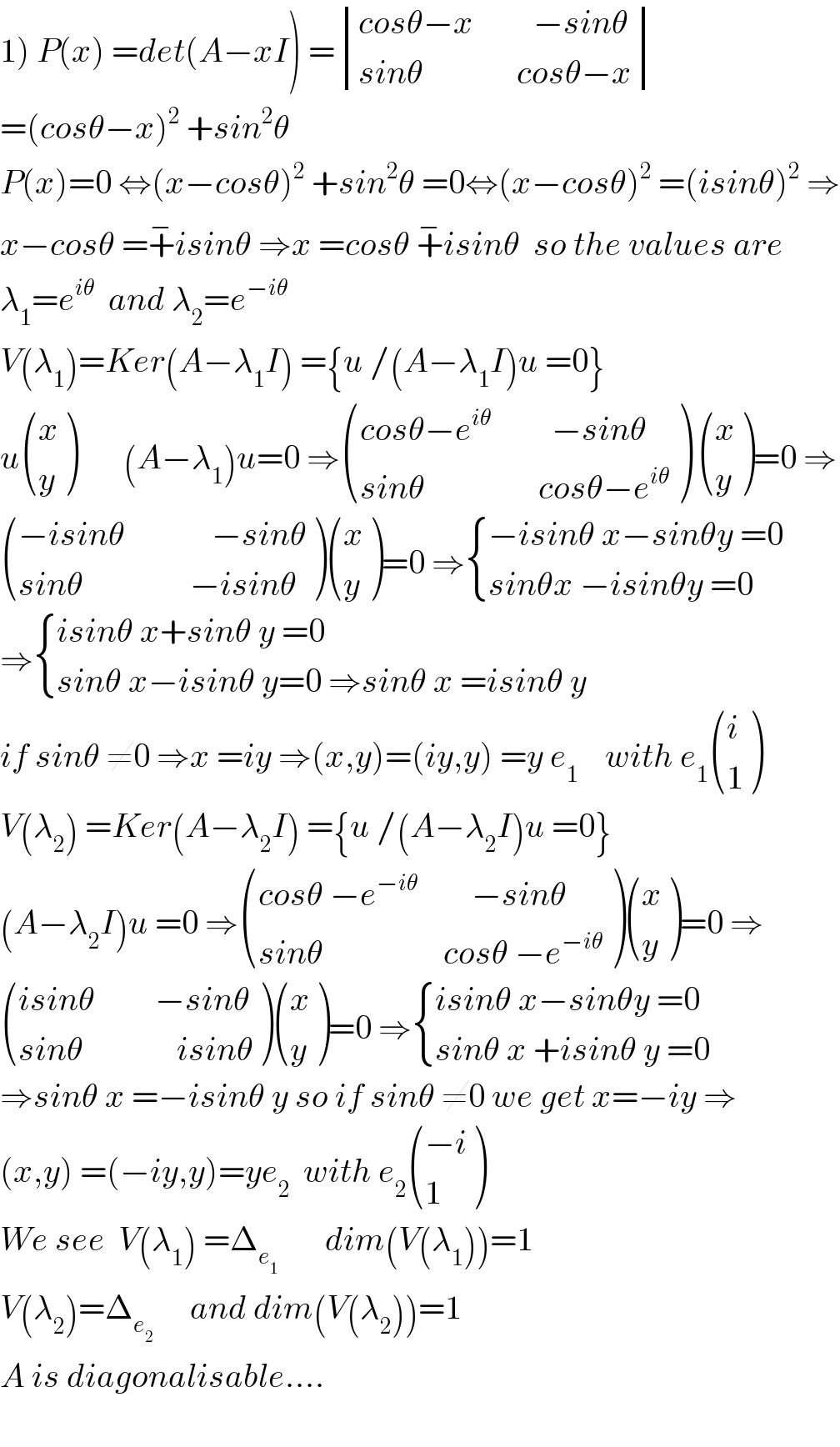 | ||
Commented by M±th+et+s last updated on 30/Apr/20 | ||
 | ||
Commented by turbo msup by abdo last updated on 30/Apr/20 | ||
 | ||