
Question Number 915 by 112358 last updated on 24/Apr/15
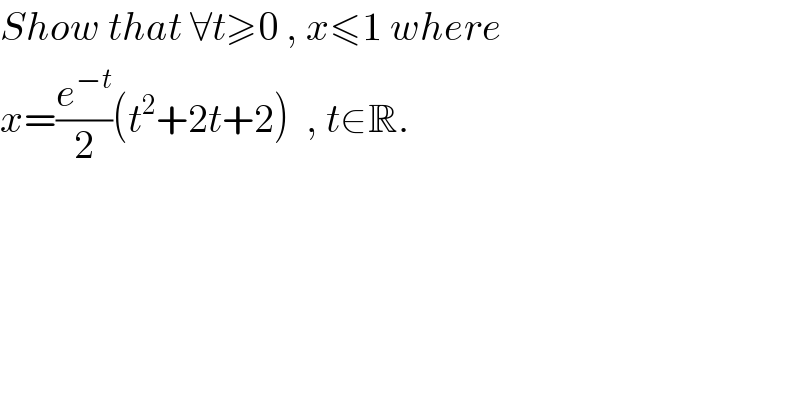
$${Show}\:{that}\:\forall{t}\geqslant\mathrm{0}\:,\:{x}\leqslant\mathrm{1}\:{where} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{{e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{2}}\left({t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)\:\:,\:{t}\in\mathbb{R}.\: \\ $$
Commented by 123456 last updated on 24/Apr/15
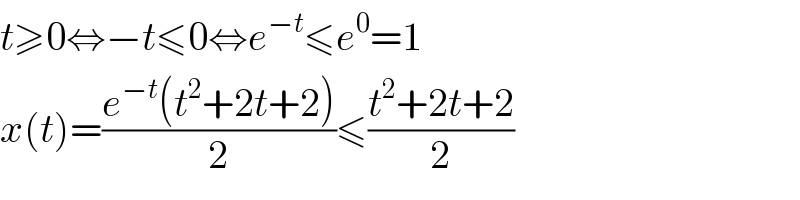
$${t}\geqslant\mathrm{0}\Leftrightarrow−{t}\leqslant\mathrm{0}\Leftrightarrow{e}^{−{t}} \leqslant{e}^{\mathrm{0}} =\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${x}\left({t}\right)=\frac{{e}^{−{t}} \left({t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{t}+\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\leqslant\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{t}+\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
Commented by 123456 last updated on 24/Apr/15

$${x}=\frac{\left({t}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{t}+\mathrm{2}\right){e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}=−\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${t}\geqslant\mathrm{0}\Leftrightarrow{e}^{−{t}} \leqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}=−\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{−{t}} }{\mathrm{2}}\leqslant−\frac{{t}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\leqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by 123456 last updated on 24/Apr/15

$$\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{shown}\:\mathrm{in}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{coments} \\ $$$${t}\geqslant\mathrm{0},\frac{{dx}}{{dt}}\leqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{so}\:{x}\left({t}\right)\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{decreasing}\:\mathrm{into}\:{t}\in\left[\mathrm{0},+\infty\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{all}\:{t}\geqslant\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}\left({t}\right)\leqslant{x}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\frac{\left(\mathrm{0}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{0}+\mathrm{2}\right){e}^{−\mathrm{0}} }{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${x}\left({t}\right)\leqslant\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{desired}\:\blacksquare \\ $$
