
Question Number 9163 by tawakalitu last updated on 21/Nov/16
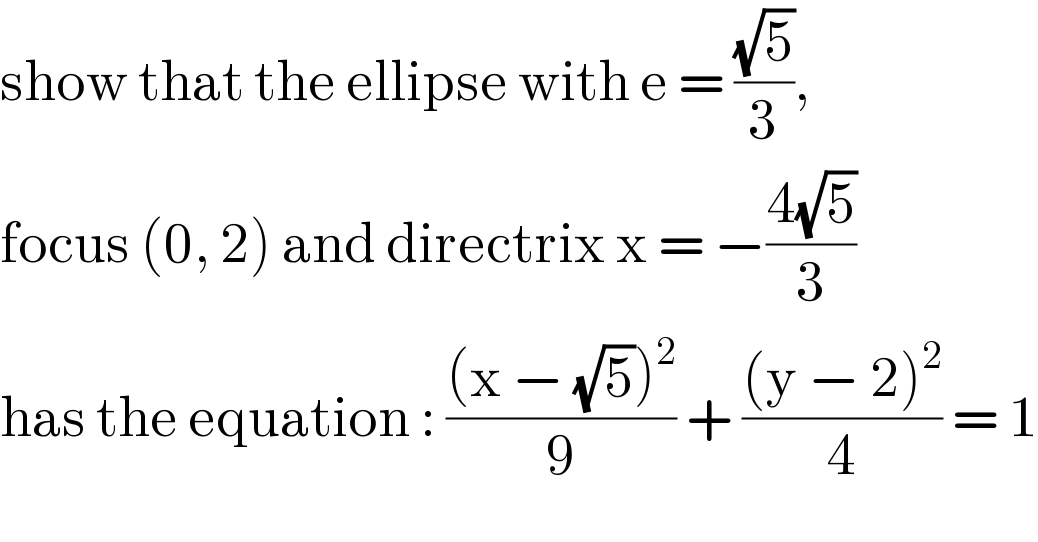
$$\mathrm{show}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{ellipse}\:\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{e}\:=\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{3}},\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{focus}\:\left(\mathrm{0},\:\mathrm{2}\right)\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{directrix}\:\mathrm{x}\:=\:−\frac{\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{has}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{equation}\::\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{x}\:−\:\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{9}}\:+\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{y}\:−\:\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}\:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by sandy_suhendra last updated on 22/Nov/16
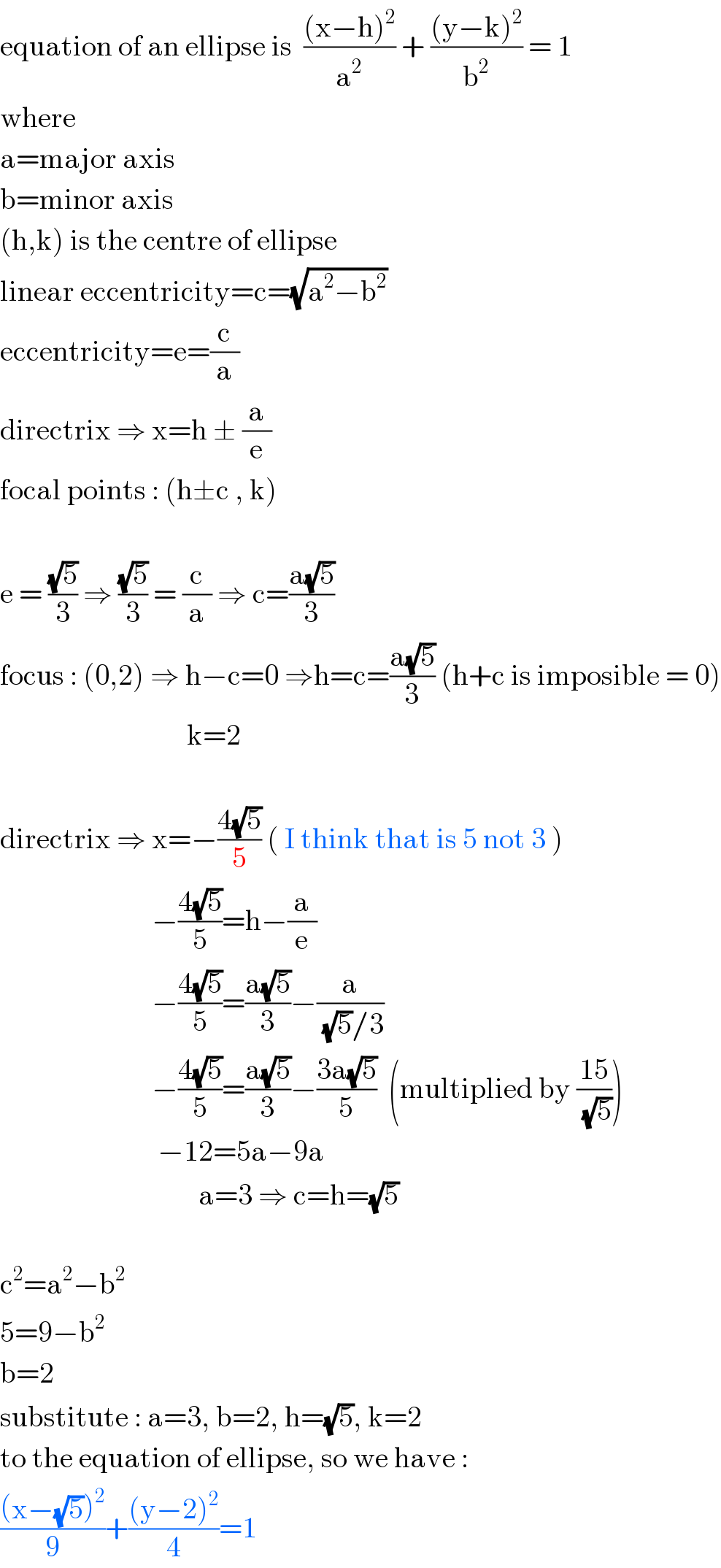
$$\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{ellipse}\:\mathrm{is}\:\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{h}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:+\:\frac{\left(\mathrm{y}−\mathrm{k}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{where}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}=\mathrm{major}\:\mathrm{axis} \\ $$$$\mathrm{b}=\mathrm{minor}\:\mathrm{axis} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{h},\mathrm{k}\right)\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{centre}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{ellipse} \\ $$$$\mathrm{linear}\:\mathrm{eccentricity}=\mathrm{c}=\sqrt{\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$\mathrm{eccentricity}=\mathrm{e}=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{a}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{directrix}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{h}\:\pm\:\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{e}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{focal}\:\mathrm{points}\::\:\left(\mathrm{h}\pm\mathrm{c}\:,\:\mathrm{k}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{e}\:=\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\Rightarrow\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{3}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{a}}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{c}=\frac{\mathrm{a}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{focus}\::\:\left(\mathrm{0},\mathrm{2}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{h}−\mathrm{c}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{h}=\mathrm{c}=\frac{\mathrm{a}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{3}}\:\left(\mathrm{h}+\mathrm{c}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{imposible}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\mathrm{directrix}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{x}=−\frac{\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{5}}\:\left(\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{think}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{5}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{3}\:\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\frac{\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{5}}=\mathrm{h}−\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{e}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\frac{\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{5}}=\frac{\mathrm{a}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}/\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\frac{\mathrm{4}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{5}}=\frac{\mathrm{a}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\mathrm{3a}\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{5}}\:\:\left(\mathrm{multiplied}\:\mathrm{by}\:\frac{\mathrm{15}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:−\mathrm{12}=\mathrm{5a}−\mathrm{9a}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{a}=\mathrm{3}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{c}=\mathrm{h}=\sqrt{\mathrm{5}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{c}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{a}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{9}−\mathrm{b}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{b}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{substitute}\::\:\mathrm{a}=\mathrm{3},\:\mathrm{b}=\mathrm{2},\:\mathrm{h}=\sqrt{\mathrm{5}},\:\mathrm{k}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{to}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{ellipse},\:\mathrm{so}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:: \\ $$$$\frac{\left(\mathrm{x}−\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{9}}+\frac{\left(\mathrm{y}−\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by tawakalitu last updated on 22/Nov/16
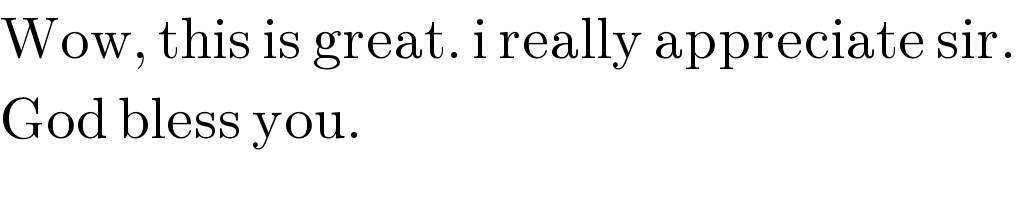
$$\mathrm{Wow},\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{great}.\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{really}\:\mathrm{appreciate}\:\mathrm{sir}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}. \\ $$
