
Question Number 91660 by Zainal Arifin last updated on 02/May/20

Commented by Prithwish Sen 1 last updated on 02/May/20

$$\mathrm{LHS} \\ $$$$\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{10}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{21}}}{\mathrm{2}}}\:+\:\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{16}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{55}}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:+\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{11}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{considering}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{only}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{the}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{positive}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{value}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{11}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:=\:\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{11}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}}\:+\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$=\:\sqrt{\frac{\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}+\sqrt{\left.\mathrm{11}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\right.}{\mathrm{2}}}\:+\sqrt{\frac{\left(\sqrt{\mathrm{7}}+\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$$=\:\sqrt{\mathrm{7}+\sqrt{\mathrm{33}}}\:+\:\sqrt{\mathrm{6}+\sqrt{\mathrm{35}}}\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{RHS}}\:\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{proved}} \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 02/May/20
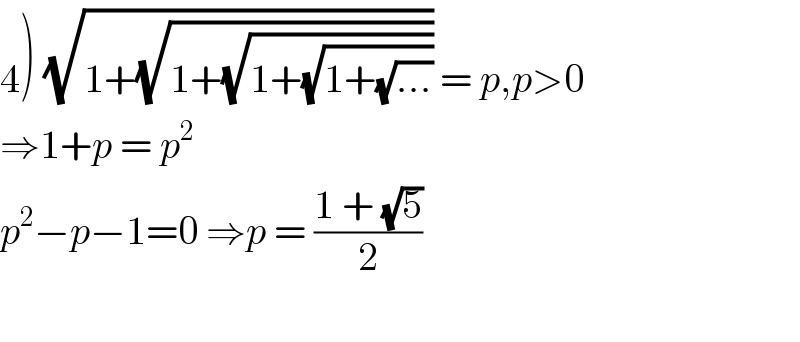
$$\left.\mathrm{4}\right)\:\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{...}}}}}\:=\:{p},{p}>\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{1}+{p}\:=\:{p}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${p}^{\mathrm{2}} −{p}−\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{p}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}\:+\:\sqrt{\mathrm{5}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by jagoll last updated on 02/May/20
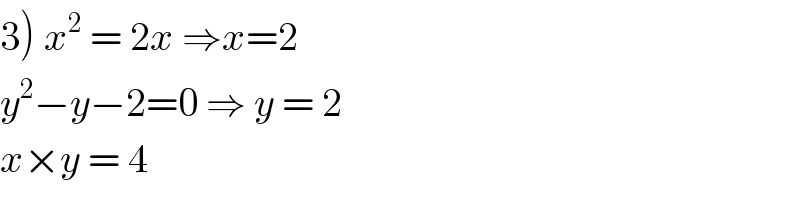
$$\left.\mathrm{3}\right)\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:=\:\mathrm{2}{x}\:\Rightarrow{x}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${y}^{\mathrm{2}} −{y}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\:{y}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${x}×{y}\:=\:\mathrm{4} \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 02/May/20
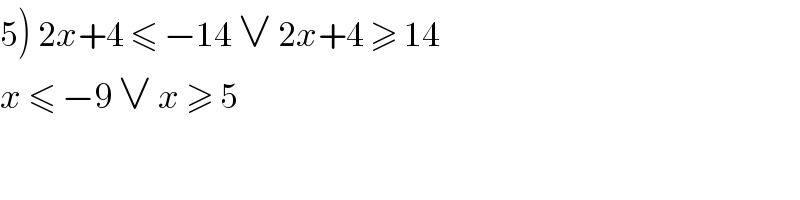
$$\left.\mathrm{5}\right)\:\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4}\:\leqslant\:−\mathrm{14}\:\vee\:\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4}\:\geqslant\:\mathrm{14}\: \\ $$$${x}\:\leqslant\:−\mathrm{9}\:\vee\:{x}\:\geqslant\:\mathrm{5} \\ $$
