
Question Number 92778 by unknown last updated on 09/May/20

Commented by prakash jain last updated on 09/May/20
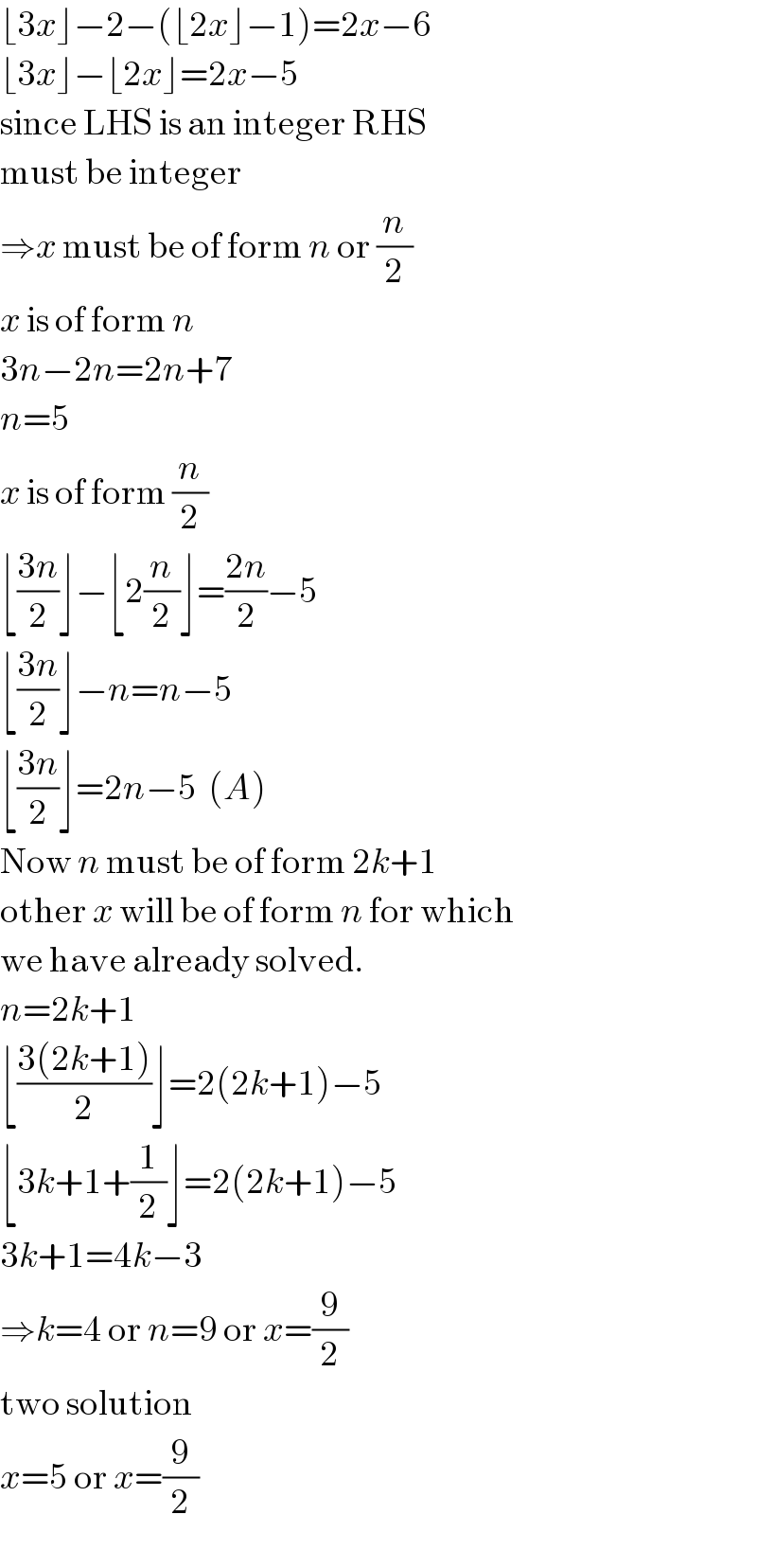
$$\lfloor\mathrm{3}{x}\rfloor−\mathrm{2}−\left(\lfloor\mathrm{2}{x}\rfloor−\mathrm{1}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\lfloor\mathrm{3}{x}\rfloor−\lfloor\mathrm{2}{x}\rfloor=\mathrm{2}{x}−\mathrm{5}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{since}\:\mathrm{LHS}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{an}\:\mathrm{integer}\:\mathrm{RHS} \\ $$$$\mathrm{must}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{integer} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}\:\mathrm{must}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{form}\:{n}\:\mathrm{or}\:\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${x}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{form}\:{n} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{n}−\mathrm{2}{n}=\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{7} \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{5}\: \\ $$$${x}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{form}\:\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\lfloor\frac{\mathrm{3}{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor−\lfloor\mathrm{2}\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor=\frac{\mathrm{2}{n}}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\lfloor\frac{\mathrm{3}{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor−{n}={n}−\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\lfloor\frac{\mathrm{3}{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor=\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{5}\:\:\left({A}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{Now}\:{n}\:\mathrm{must}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{form}\:\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\mathrm{other}\:{x}\:\mathrm{will}\:\mathrm{be}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{form}\:{n}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{which} \\ $$$$\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{already}\:\mathrm{solved}. \\ $$$${n}=\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\lfloor\frac{\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor=\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\lfloor\mathrm{3}{k}+\mathrm{1}+\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\rfloor=\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{2}{k}+\mathrm{1}\right)−\mathrm{5} \\ $$$$\mathrm{3}{k}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{4}{k}−\mathrm{3} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{k}=\mathrm{4}\:\mathrm{or}\:{n}=\mathrm{9}\:\mathrm{or}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{two}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{5}\:\mathrm{or}\:{x}=\frac{\mathrm{9}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
