
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 94418 by niroj last updated on 18/May/20

Answered by som(math1967) last updated on 18/May/20
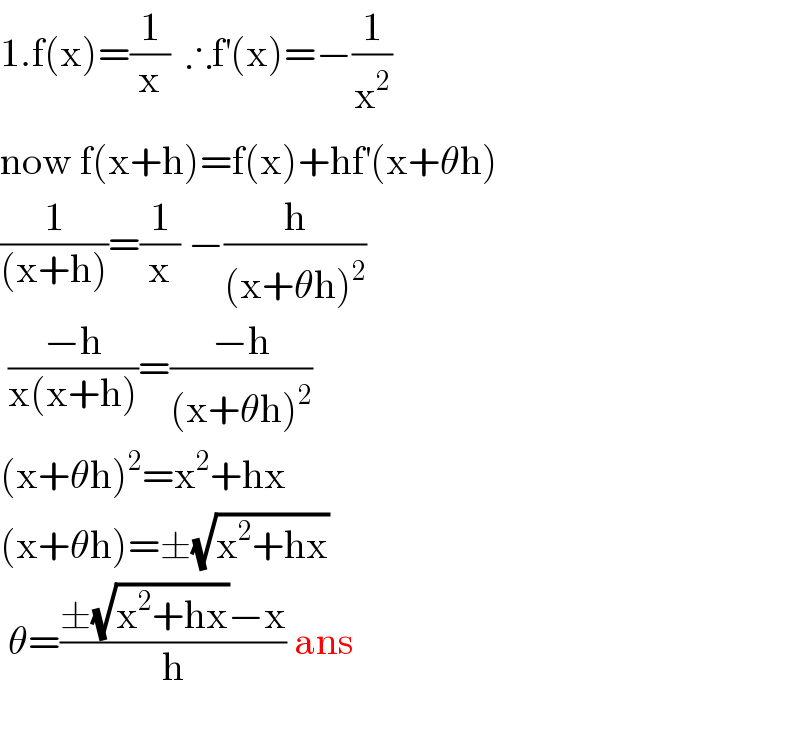
Commented by niroj last updated on 18/May/20
nice ����thank you.
Answered by som(math1967) last updated on 18/May/20
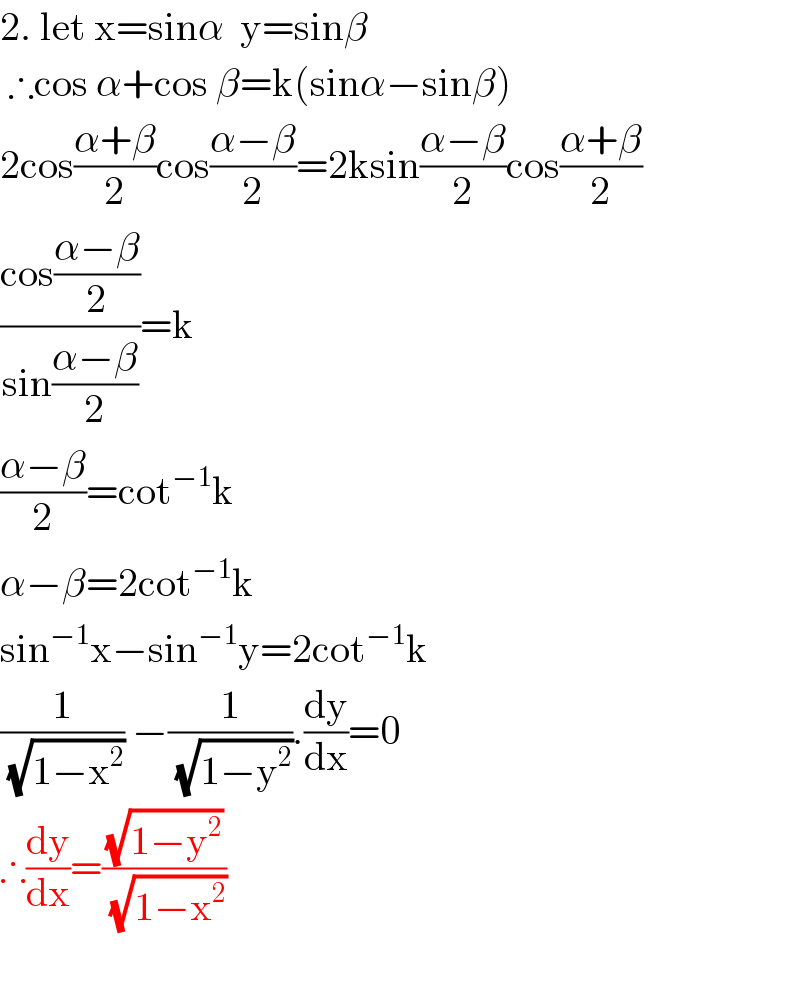
Commented by niroj last updated on 18/May/20
superb������ thank dear for your effort.
Answered by Mr.D.N. last updated on 18/May/20
![3. x^2 (d^2 y/dx^2 ) −3x(dy/dx)+3y = x^2 (2x−1) Second order linear differential eq^n with variable coefficient (d^2 y/dx^2 )− (3/x) (dy/dx)+(3/x^2 )y = 2x−1.....(i) P= −(3/x), Q= (3/x^2 ) and R= 2x−1 If P+Qx =0 then Part of CF u=x −(3/x)+(3/x^2 )x=0 for complete sol^n : y=uv y= vx.......(ii) We know the form : (d^2 v/dx^2 )+(P +(2/u).(du/dx))(dv/dx)= (R/u) (d^2 v/dx^2 )+( −(3/x)+(2/x).(dx/dx))(dv/dx)= ((2x−1)/x) (d^2 v/dx^2 ) −(1/x).(dv/dx)= ((2x−1)/x) Change to linear form, Put , (dv/dx)= t ⇒ (d^2 v/dx^2 )= (dt/dx) (dt/dx)− (1/x)t = ((2x−1)/x) Now, IF= e^(∫Pdx) = e^(−∫(1/x)dx) =e^(−log x) IF= e^(log x^(−1) ) = (1/x) t.(1/x) = ∫(1/x).((2x−1)/x)dx+C_1 (t/x)= ∫((2/x)−x^(−2) )dx+C_1 t.(1/x)= 2log x −(x^(−1) /((−1)))+C_1 t.(1/x)= 2log x +(1/x)+C_1 t= 2xlog x+1+C_1 x (dv/dx)= 2x log x +1+C_1 x ∫dv = 2∫x log x dx+∫dx +C_1 ∫xdx+C_2 v= 2[ log x.(x^2 /2)−∫(1/x).(x^2 /2)dx]+x+(x^2 /2)C_1 +C_2 v= 2.(x^2 /2)log x −2.(1/2)∫xdx+x+(x^2 /2)C_1 +C_2 v = x^2 log x−(x^2 /2)+x+(x^2 /2)C_1 +C_2 Now again Putting the value of v in equ^n (ii) y= vx y = x^3 log x−(x^3 /2)+x^2 +(x^3 /2)C_1 +C_2 x .](Q94438.png)
Commented by niroj last updated on 18/May/20
it's outstanding��������
Commented by peter frank last updated on 24/May/20

