
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 94739 by 174 last updated on 20/May/20

Commented by i jagooll last updated on 20/May/20
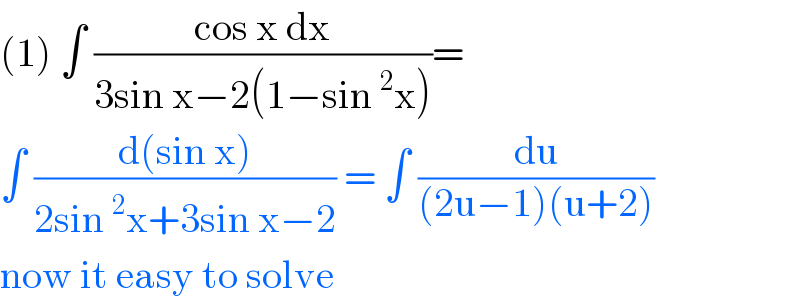
Commented by PRITHWISH SEN 2 last updated on 20/May/20
![3)put sinx=(√2)t⇒cosxdx=(√2) dt ∫(dt/((√2)(1+t^2 ))) = (1/(√2)) tan^(−1) (((sin x)/(√2)) )+C 4) ∫sec^2 xdx+∫tan^2 x dx = 2∫sec^2 x dx −∫dx = 2tan x−x+C 5)∫[x+ln(e−x)]dx= (x^2 /2)+xln(e−x)+∫(x/(e−x))dx = (x^2 /2)+xln(e−x)−eln(e−x)−x+C](Q94746.png)
Answered by Rio Michael last updated on 20/May/20
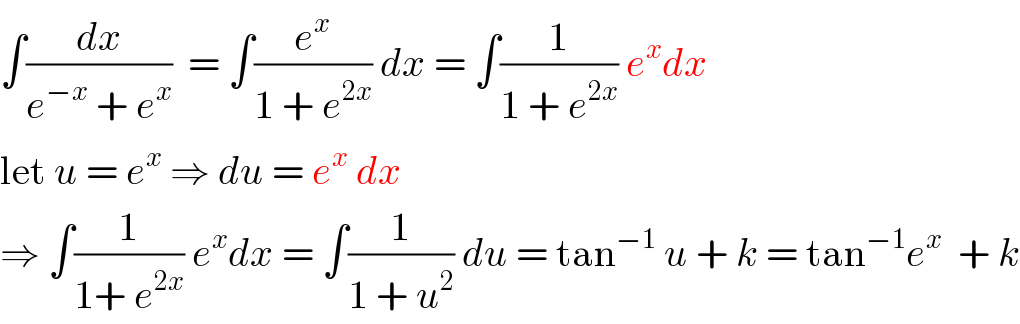
Answered by i jagooll last updated on 20/May/20
![(2) ∫ (e^x /(1+e^(2x) )) dx = ∫ (du/(1+u^2 )) , [ u = e^x ] = tan^(−1) (u) + c = tan^(−1) (e^x ) + c](Q94745.png)
