
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 95397 by ~blr237~ last updated on 25/May/20
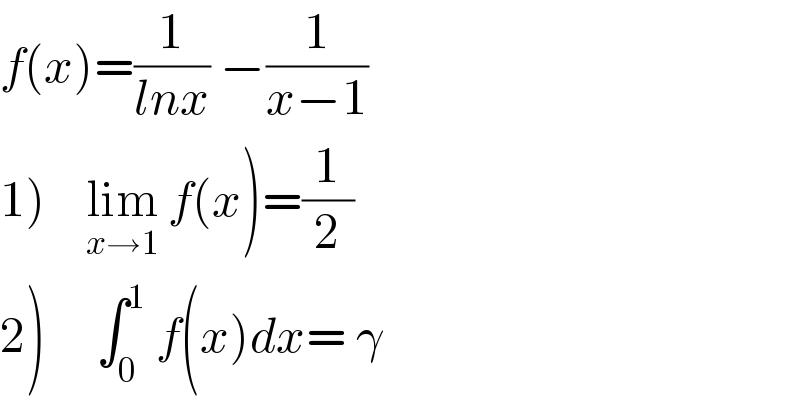
Commented by Mikael_786 last updated on 25/May/20
![1. lim_(x→1) {(1/(lnx))−(1/(x−1))} lim_(x→1) {(1/(x−1))(((x−1)/(lnx))−1)}=lim_(x→1) {(1/(x−1))(∫_0 ^1 x^y dy−1)} lim_(x→1) {∫_0 ^1 (x^y /(x−1))dy−∫_0 ^1 (1/(x−1))dy} lim_(x→1) {∫_0 ^1 ((x^y −1)/(x−1))dy}=∫_0 ^1 {lim_(x→1) ((x^y −1)/(x−1))}dy =∫_0 ^1 ydy=[(y^2 /2)]_0 ^1 =(1/2)](Q95519.png)
Commented by Mikael_786 last updated on 25/May/20
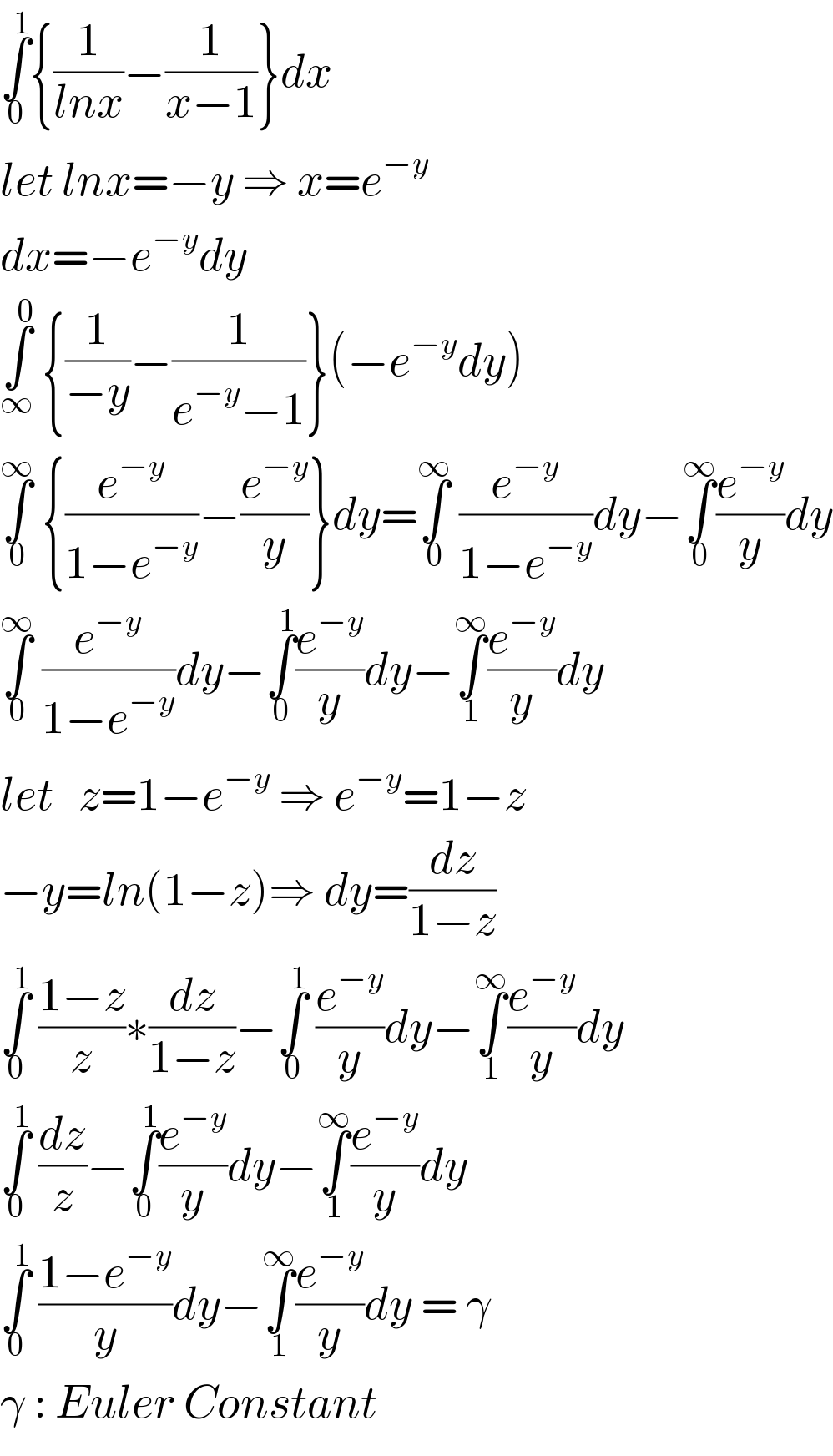
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 95397 by ~blr237~ last updated on 25/May/20 | ||
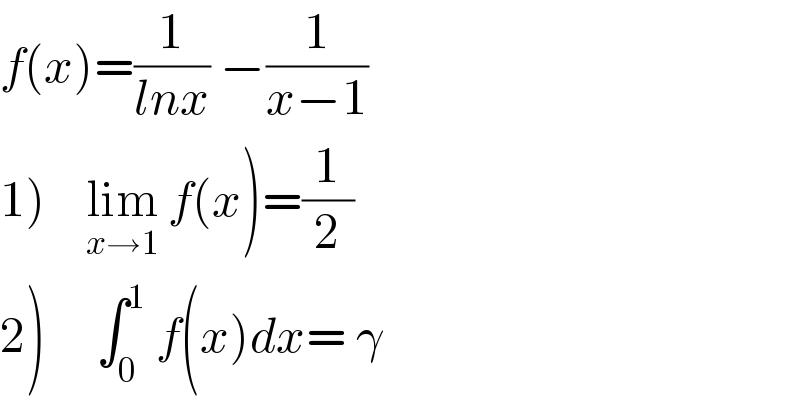 | ||
Commented by Mikael_786 last updated on 25/May/20 | ||
![1. lim_(x→1) {(1/(lnx))−(1/(x−1))} lim_(x→1) {(1/(x−1))(((x−1)/(lnx))−1)}=lim_(x→1) {(1/(x−1))(∫_0 ^1 x^y dy−1)} lim_(x→1) {∫_0 ^1 (x^y /(x−1))dy−∫_0 ^1 (1/(x−1))dy} lim_(x→1) {∫_0 ^1 ((x^y −1)/(x−1))dy}=∫_0 ^1 {lim_(x→1) ((x^y −1)/(x−1))}dy =∫_0 ^1 ydy=[(y^2 /2)]_0 ^1 =(1/2)](Q95519.png) | ||
Commented by Mikael_786 last updated on 25/May/20 | ||
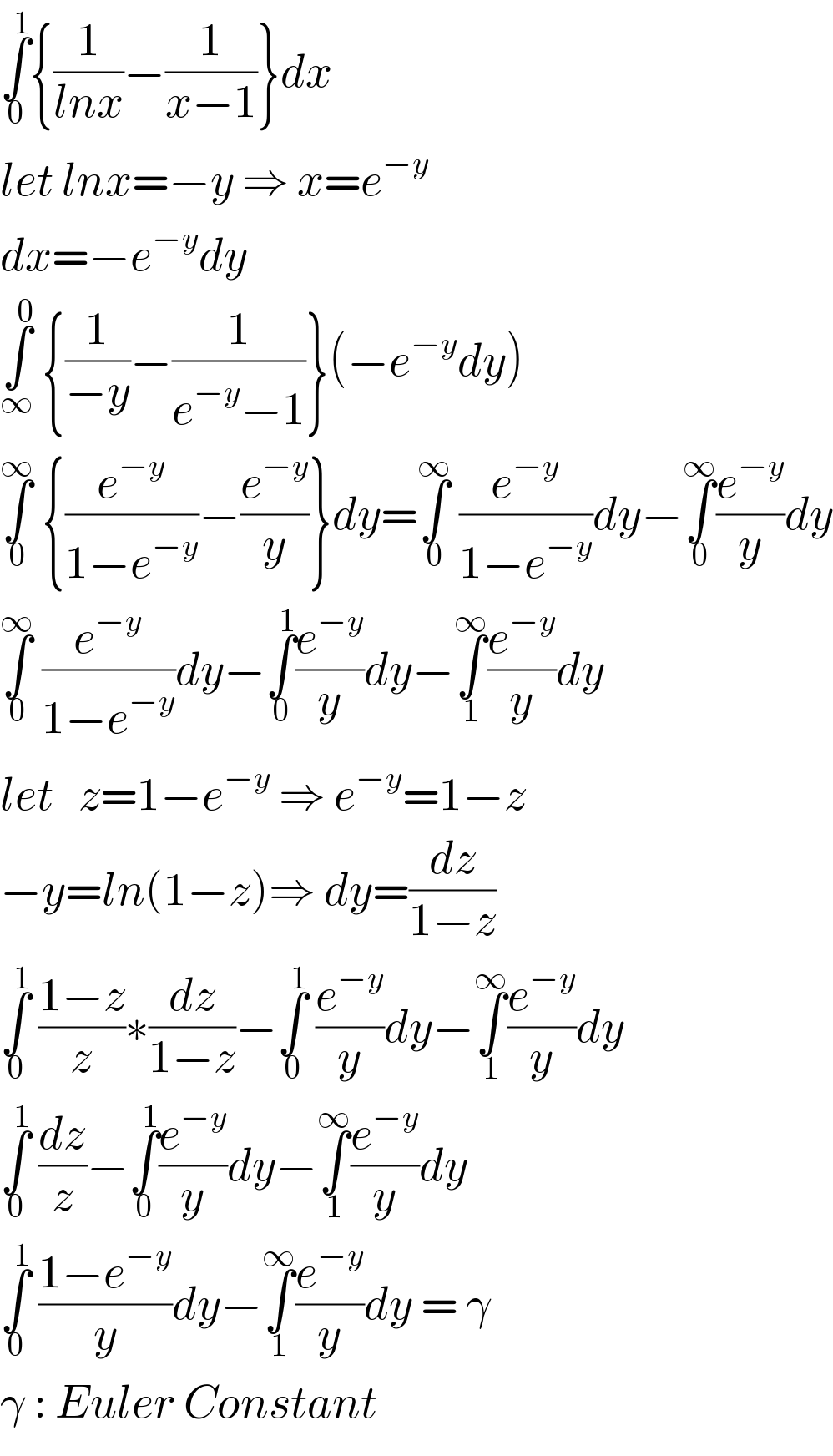 | ||