
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 95485 by O Predador last updated on 25/May/20

Commented by PRITHWISH SEN 2 last updated on 25/May/20
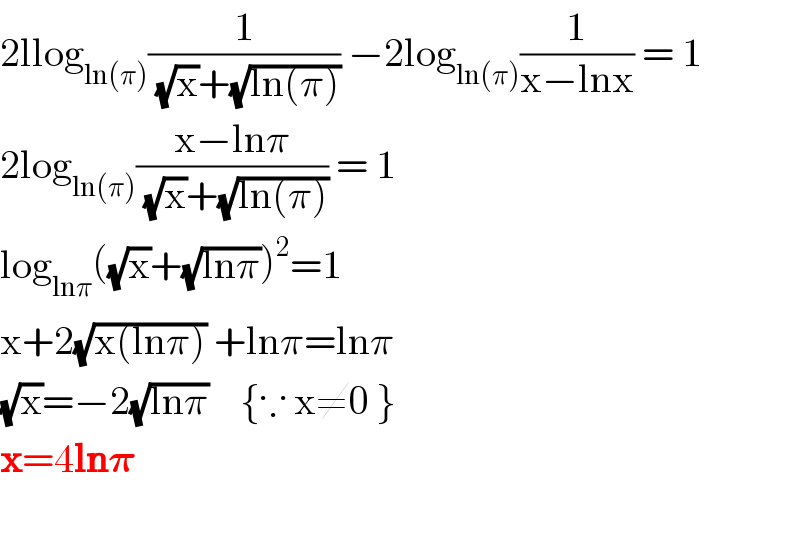
Commented by O Predador last updated on 25/May/20

| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 95485 by O Predador last updated on 25/May/20 | ||
 | ||
Commented by PRITHWISH SEN 2 last updated on 25/May/20 | ||
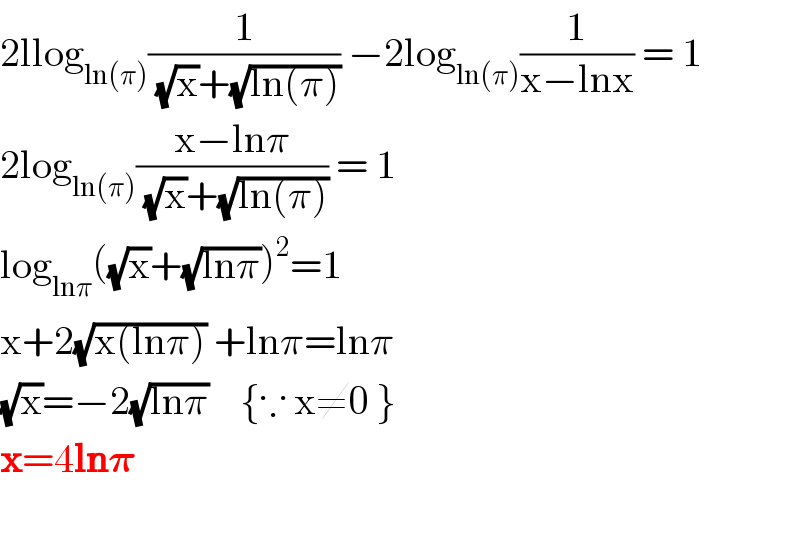 | ||
Commented by O Predador last updated on 25/May/20 | ||
 | ||