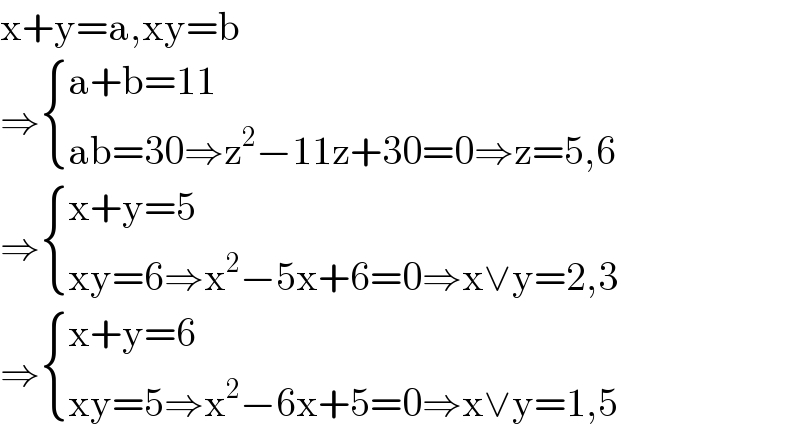Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 95608 by bobhans last updated on 26/May/20

Commented by john santu last updated on 26/May/20
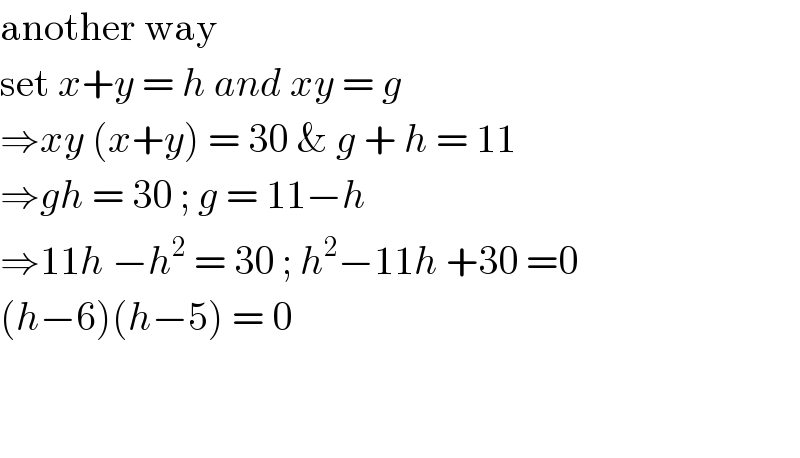
Commented by bobhans last updated on 26/May/20

Answered by john santu last updated on 26/May/20
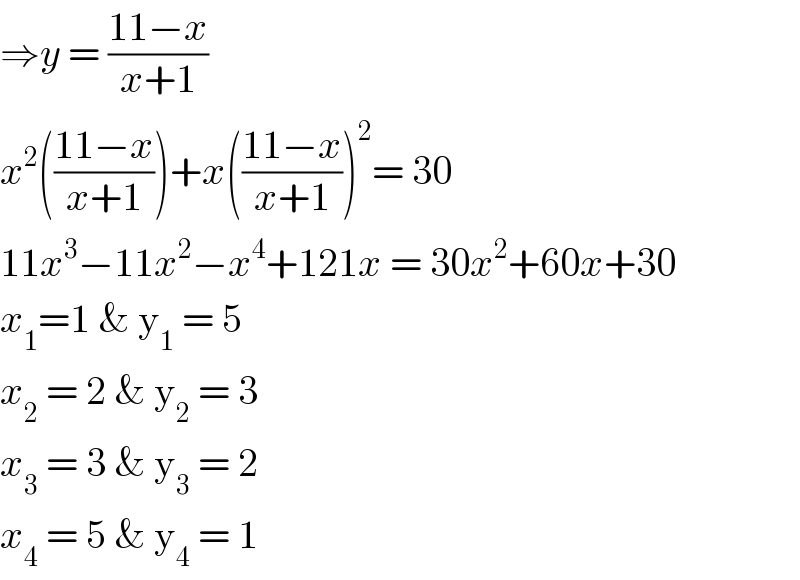
Answered by MJS last updated on 26/May/20
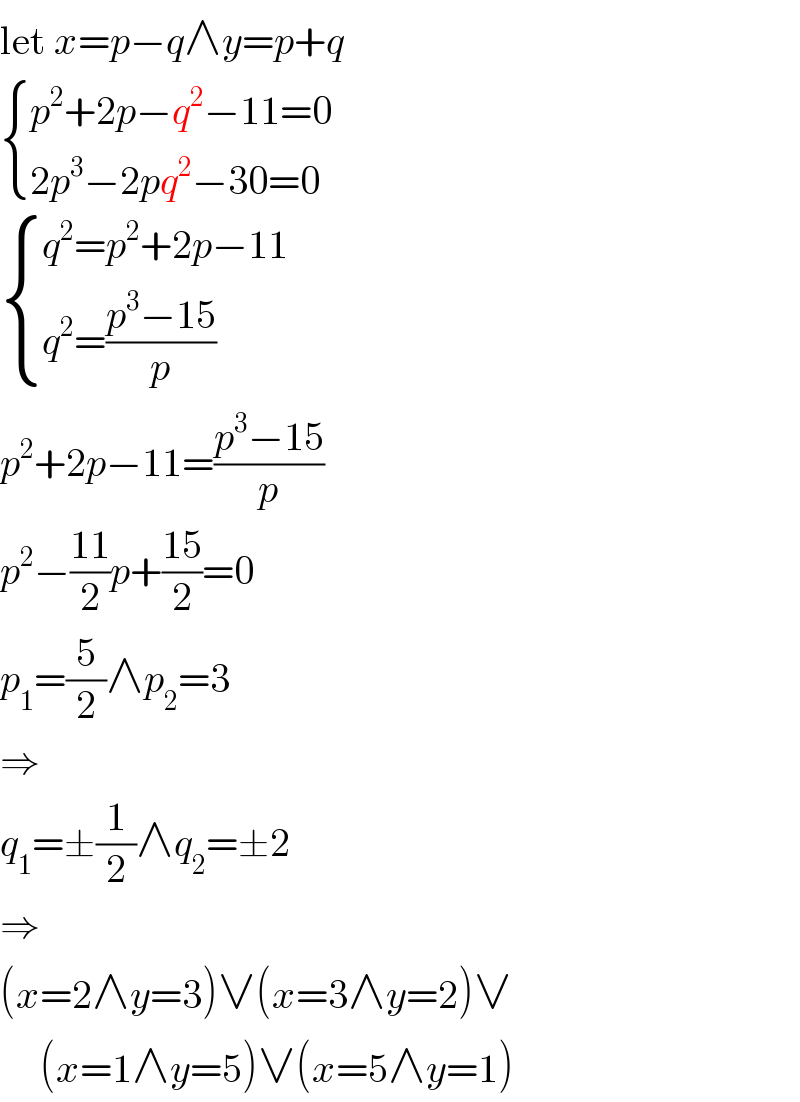
Answered by behi83417@gmail.com last updated on 26/May/20