
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 95662 by john santu last updated on 26/May/20

$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{p}\right)\:+\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{p}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{6x}−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{20}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{29p} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{p}\right)}{\mathrm{2p}}\:=\:? \\ $$
Commented by i jagooll last updated on 26/May/20
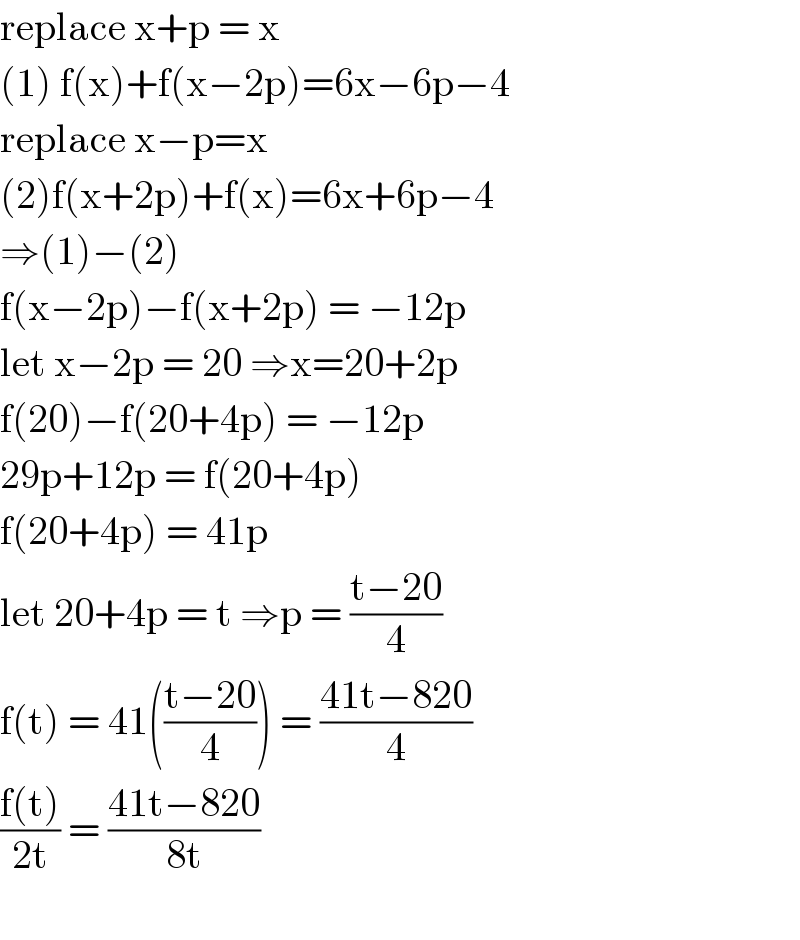
$$\mathrm{replace}\:\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{p}\:=\:\mathrm{x}\: \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)+\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2p}\right)=\mathrm{6x}−\mathrm{6p}−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{replace}\:\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{p}=\mathrm{x} \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2p}\right)+\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{6x}+\mathrm{6p}−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\left(\mathrm{1}\right)−\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2p}\right)−\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2p}\right)\:=\:−\mathrm{12p} \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2p}\:=\:\mathrm{20}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{x}=\mathrm{20}+\mathrm{2p} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{20}\right)−\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{20}+\mathrm{4p}\right)\:=\:−\mathrm{12p} \\ $$$$\mathrm{29p}+\mathrm{12p}\:=\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{20}+\mathrm{4p}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{20}+\mathrm{4p}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{41p} \\ $$$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{20}+\mathrm{4p}\:=\:\mathrm{t}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{p}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{t}−\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{41}\left(\frac{\mathrm{t}−\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{4}}\right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{41t}−\mathrm{820}}{\mathrm{4}} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{t}\right)}{\mathrm{2t}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{41t}−\mathrm{820}}{\mathrm{8t}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\: \\ $$
Commented by PRITHWISH SEN 2 last updated on 26/May/20

$$\mathrm{put}\:\mathrm{p}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{2f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{6x}−\mathrm{4}\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{2}\Rightarrow\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{20}\right)=\mathrm{58} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\mathrm{p}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\therefore\frac{\boldsymbol{\mathrm{f}}\left(\boldsymbol{\mathrm{p}}\right)}{\mathrm{2}\boldsymbol{\mathrm{p}}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{3}×\mathrm{2}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{2}×\mathrm{2}}\:=\mathrm{1}\:\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{please}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{check}} \\ $$
Commented by i jagooll last updated on 27/May/20

$$\mathrm{how}\:\mathrm{can}\:\mathrm{p}\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{p}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\:? \\ $$$$\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{meant}\:\mathrm{0}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\:? \\ $$
Commented by PRITHWISH SEN 2 last updated on 27/May/20

$$\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{1st}\:\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{p}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{point}\:\mathrm{which}\:\mathrm{can}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{take}\:\mathrm{any}\:\mathrm{value}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{But}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{second}\:\mathrm{equation}\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{constant}.\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{now}\:\mathrm{fixed}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{p}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{2}\:\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{get} \\ $$$$\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)=\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\mathrm{then}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)+\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{2}+\mathrm{3}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{2}\right)−\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\:\mathrm{6x}−\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\mathrm{and}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{20}\right)=\:\mathrm{3}×\mathrm{20}−\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{58}=\mathrm{29p}\:\:\mathrm{where}\:\mathrm{p}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by i jagooll last updated on 27/May/20
$$\mathrm{alright}\:\mathrm{sir}.\:\mathrm{thank}\:\mathrm{you} \\ $$
Answered by john santu last updated on 28/May/20
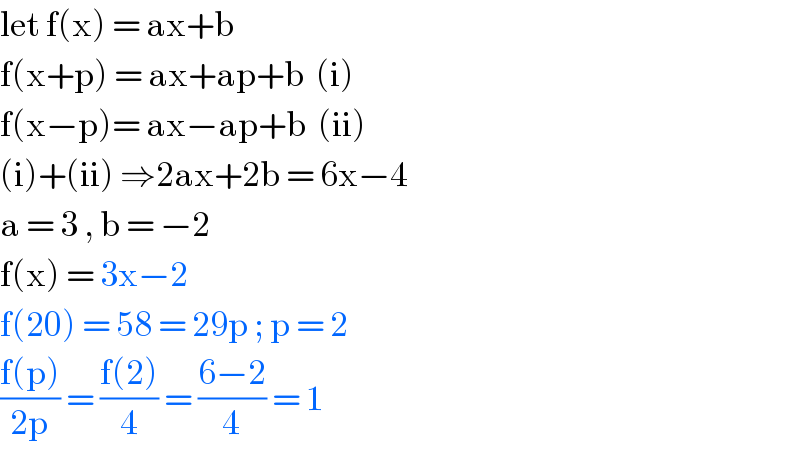
$$\mathrm{let}\:\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{ax}+\mathrm{b}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{p}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{ax}+\mathrm{ap}+\mathrm{b}\:\:\left(\mathrm{i}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}−\mathrm{p}\right)=\:\mathrm{ax}−\mathrm{ap}+\mathrm{b}\:\:\left(\mathrm{ii}\right) \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{i}\right)+\left(\mathrm{ii}\right)\:\Rightarrow\mathrm{2ax}+\mathrm{2b}\:=\:\mathrm{6x}−\mathrm{4}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\:=\:\mathrm{3}\:,\:\mathrm{b}\:=\:−\mathrm{2}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{3x}−\mathrm{2}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{20}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{58}\:=\:\mathrm{29p}\:;\:\mathrm{p}\:=\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{p}\right)}{\mathrm{2p}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{4}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{6}−\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{4}}\:=\:\mathrm{1}\: \\ $$
