
Question Number 96542 by Hamida last updated on 02/Jun/20

Commented by bobhans last updated on 02/Jun/20
![average rate = (1/(3−(−3))) ∫_(−3) ^3 (x^2 −2) dx = (1/6) [(1/3)x^3 −2x]_(−3) ^3 =(1/6)((1/3)(54)−2(6)) = (1/6)(18−12) = 1](Q96546.png)
$$\mathrm{average}\:\mathrm{rate}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}−\left(−\mathrm{3}\right)}\:\underset{−\mathrm{3}} {\overset{\mathrm{3}} {\int}}\left(\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{2}\right)\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\:\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\mathrm{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{2x}\right]_{−\mathrm{3}} ^{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{3}}\left(\mathrm{54}\right)−\mathrm{2}\left(\mathrm{6}\right)\right)\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{6}}\left(\mathrm{18}−\mathrm{12}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 02/Jun/20
![f(x) is even function, therefore average rate of change over [−a,a] is always zero.](Q96582.png)
$${f}\left({x}\right)\:{is}\:{even}\:{function},\:{therefore} \\ $$$${average}\:{rate}\:{of}\:{change}\:{over}\:\left[−{a},{a}\right] \\ $$$${is}\:{always}\:{zero}. \\ $$
Commented by john santu last updated on 02/Jun/20
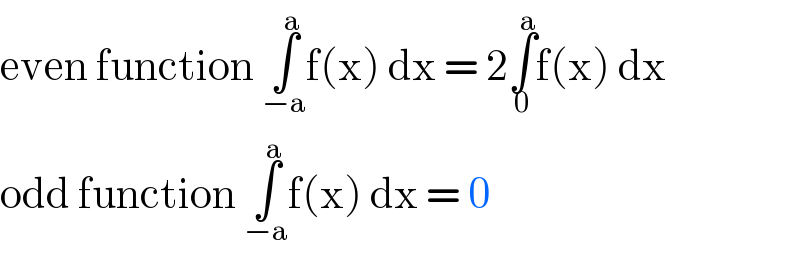
$$\mathrm{even}\:\mathrm{function}\:\underset{−\mathrm{a}} {\overset{\mathrm{a}} {\int}}\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:\mathrm{dx}\:=\:\mathrm{2}\underset{\mathrm{0}} {\overset{\mathrm{a}} {\int}}\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:\mathrm{dx} \\ $$$$\mathrm{odd}\:\mathrm{function}\:\underset{−\mathrm{a}} {\overset{\mathrm{a}} {\int}}\mathrm{f}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:\mathrm{dx}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 03/Jun/20
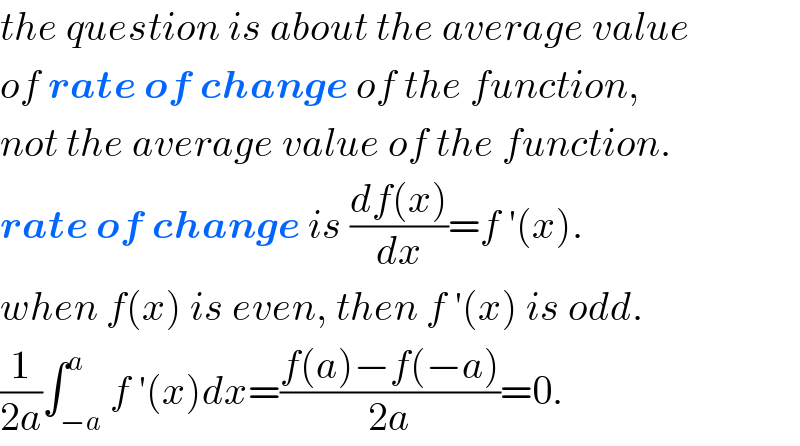
$${the}\:{question}\:{is}\:{about}\:{the}\:{average}\:{value} \\ $$$${of}\:\boldsymbol{{rate}}\:\boldsymbol{{of}}\:\boldsymbol{{change}}\:{of}\:{the}\:{function}, \\ $$$${not}\:{the}\:{average}\:{value}\:{of}\:{the}\:{function}. \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{{rate}}\:\boldsymbol{{of}}\:\boldsymbol{{change}}\:{is}\:\frac{{df}\left({x}\right)}{{dx}}={f}\:'\left({x}\right). \\ $$$${when}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:{is}\:{even},\:{then}\:{f}\:'\left({x}\right)\:{is}\:{odd}. \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}{a}}\int_{−{a}} ^{{a}} {f}\:'\left({x}\right){dx}=\frac{{f}\left({a}\right)−{f}\left(−{a}\right)}{\mathrm{2}{a}}=\mathrm{0}. \\ $$
Commented by bobhans last updated on 03/Jun/20

$$\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{wrong}\:\mathrm{mr}\:\mathrm{W}.\:\mathrm{it}\:\mathrm{odd}\:\mathrm{function} \\ $$$$\overset{−} {\mathrm{f}}\left(\mathrm{x}\right)\:=\:\mathrm{0}\:,\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{even}\:\mathrm{function} \\ $$
Commented by Hamida last updated on 03/Jun/20

$${Thank}\:{you}\: \\ $$
