
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 97418 by Rio Michael last updated on 08/Jun/20
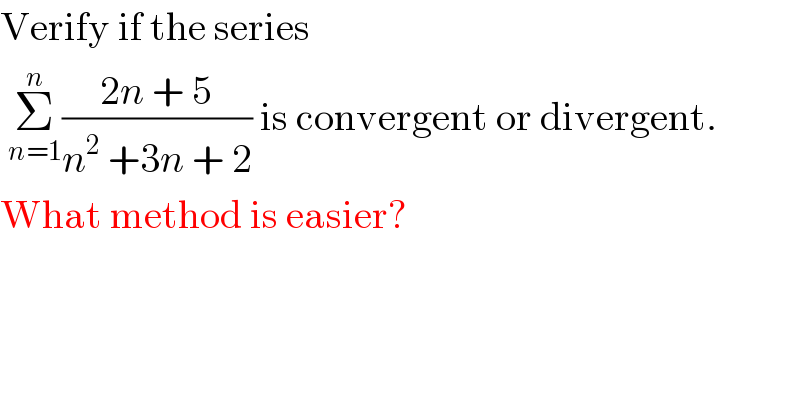
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 08/Jun/20
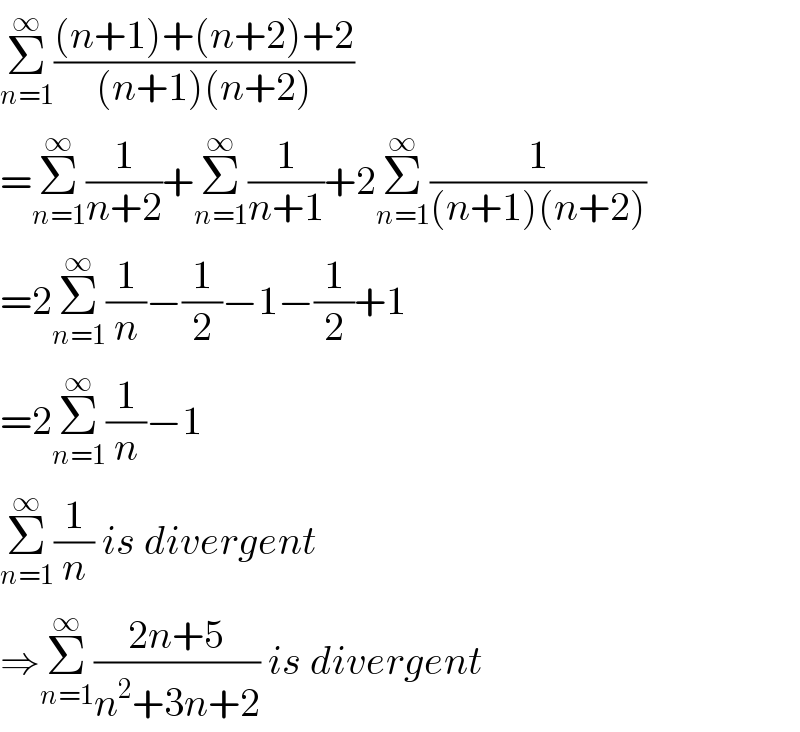
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 08/Jun/20

Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 08/Jun/20
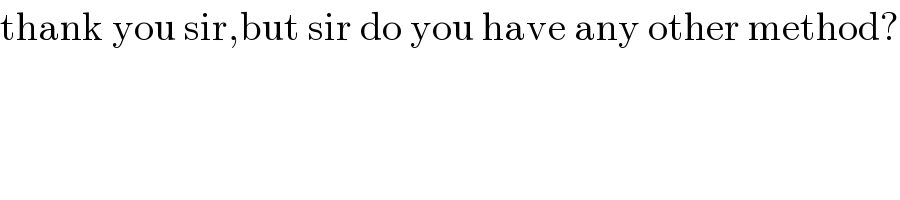
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 97418 by Rio Michael last updated on 08/Jun/20 | ||
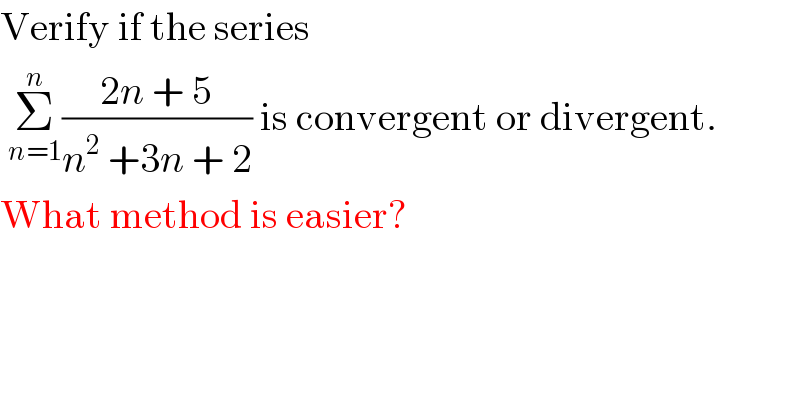 | ||
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 08/Jun/20 | ||
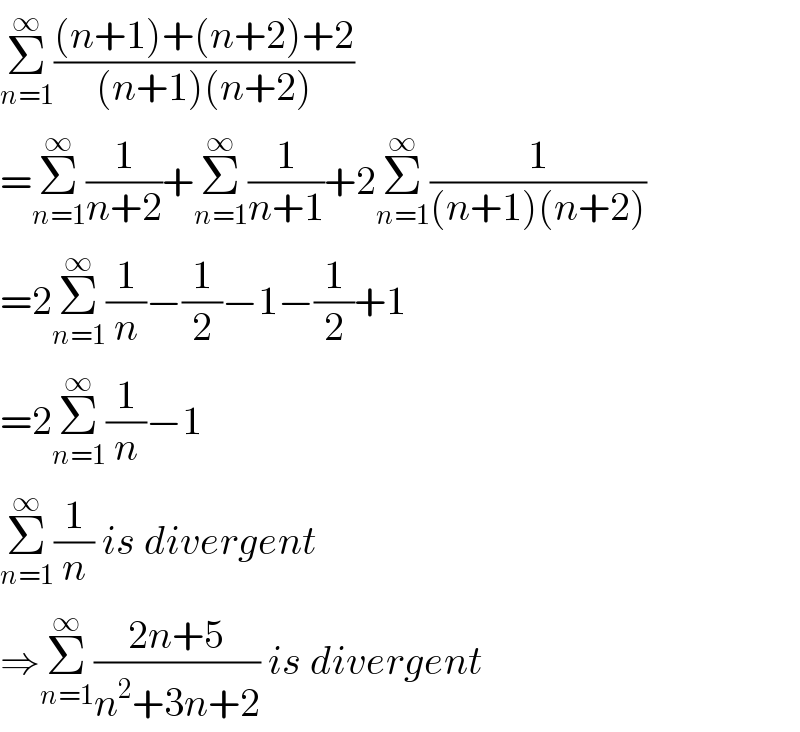 | ||
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 08/Jun/20 | ||
 | ||
| ||
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 08/Jun/20 | ||
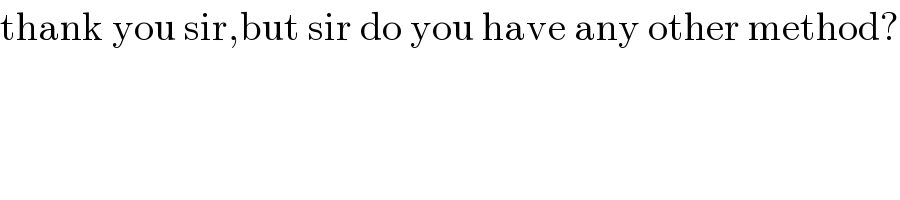 | ||