
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 98267 by M±th+et+s last updated on 12/Jun/20

Answered by maths mind last updated on 13/Jun/20
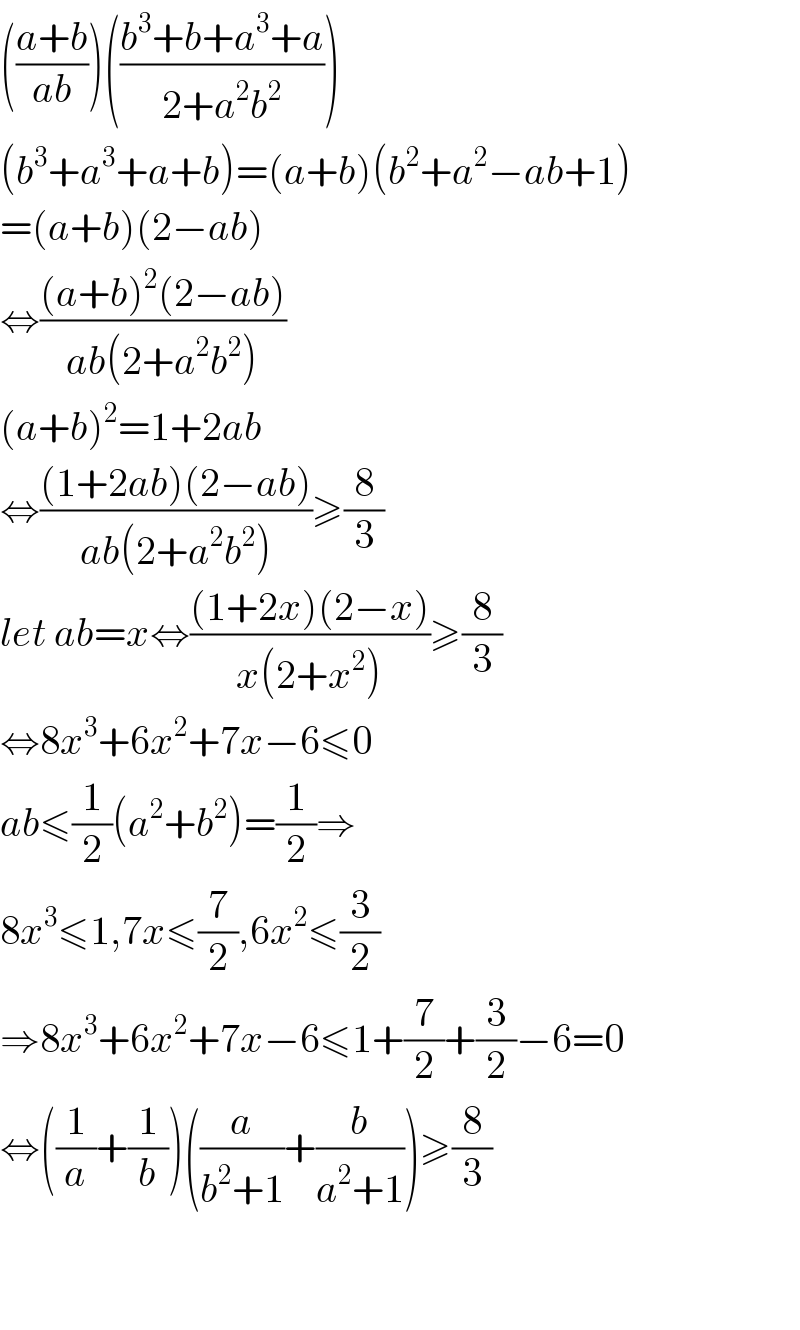
Commented by M±th+et+s last updated on 13/Jun/20
������ great work
Commented bymaths mind last updated on 13/Jun/20
Commented by M±th+et+s last updated on 13/Jun/20
Answered by 1549442205 last updated on 13/Jun/20
![Putting a=cosϕ,b=sinϕ,ϕ∈[0;(π/2)].Then the given inequality becomes ((1/(cosϕ))+(1/(sinϕ)))(((sinϕ)/(cos^2 ϕ+1))+((cosϕ)/(sin^2 ϕ+1)))≥(8/3) ⇔(((cosϕ+sinϕ)(cos^3 ϕ+sin^3 ϕ+cosϕ+sinϕ))/(cosϕ.sinϕ(2+cos^2 ϕsin^2 ϕ)))≥(8/3) ⇔(((cosϕ+sinϕ)^2 (2−sinϕcosϕ))/(((sin2ϕ)/2).(2+((sin^2 ϕ)/4))))≥(8/3) ⇔(((1+sin2ϕ)(2−((sin2ϕ)/2)))/(sin2ϕ+((sin^3 ϕ)/8)))≥(8/3) ⇔3{2+(3/2)sin2ϕ−((sin^2 2ϕ)/2)}≥8sin2ϕ+sin^3 2ϕ ⇔sin^3 2ϕ+(3/2)sin^2 2ϕ+(7/2)sin2ϕ−6≤0 ⇔2sin^3 2ϕ+3sin^2 2ϕ+7sin2ϕ−12≤0 ⇔(sin2ϕ−1)(2sin^2 2ϕ+5sin2ϕ+12)≤0 The final inequality is always true because (2sin^2 2ϕ+5sin2ϕ+12)=2(sin2ϕ+(5/4))^2 +((71)/8)>0 and sin2ϕ≤1.Therefore the given inequality proved.The equality occurs if and only if sin2ϕ=1⇔a=b=((√2)/2)](Q98360.png)
Commented by M±th+et+s last updated on 13/Jun/20

