
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 99072 by Mr.D.N. last updated on 18/Jun/20

Answered by mr W last updated on 18/Jun/20
![∫((x^2 +2x−1)/(2x^2 +3x+1))dx =(1/2)∫((2x^2 +4x−2)/(2x^2 +3x+1))dx =(1/2)∫((2x^2 +3x+1+x−3)/(2x^2 +3x+1))dx =(1/2)∫[1+(1/4)(((4x+3−15)/(2x^2 +3x+1)))]dx =(1/2)∫[1+(1/4)(((4x+3)/(2x^2 +3x+1)))−((15)/2)×(1/((2x+1)(2x+2)))]dx =(1/2){∫dx+(1/4)∫((d(2x^2 +3x+1))/(2x^2 +3x+1))−((15)/4)×∫((1/(2x+1))−(1/(2x+2)))d(2x)} =(1/2){x+(1/4)ln (2x^2 +3x+1)−((15)/4)ln ((2x+1)/(2(x+1)))}+C =(x/2)+(1/8)ln (2x+1)(x+1)−((15)/8)ln ((2x+1)/(x+1))+C =(x/2)−(7/4)ln (2x+1)+2 ln (x+1)+C](Q99073.png)
Commented by Mr.D.N. last updated on 18/Jun/20
awesome thank you mr. W keep rocking��������✍��
Commented by niroj last updated on 18/Jun/20
what grate deal.��
Answered by maths mind last updated on 18/Jun/20

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 18/Jun/20

Commented by Mr.D.N. last updated on 18/Jun/20
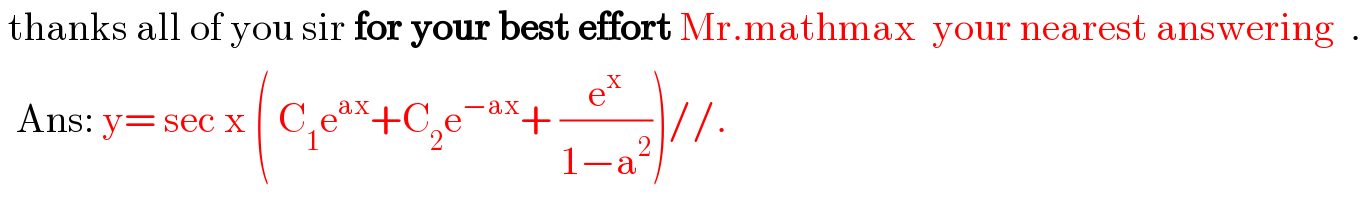
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 18/Jun/20

