
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 99413 by maths mind last updated on 20/Jun/20
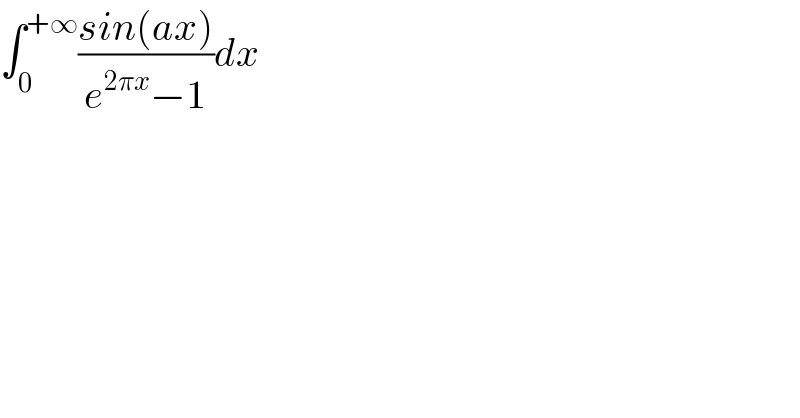
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 20/Jun/20
![I =∫_0 ^∞ ((sin(ax))/(e^(2πx) −1))dx ⇒I = ∫_0 ^∞ ((e^(−2πx) sin(ax))/(1−e^(−2πx) )) =∫_0 ^∞ e^(−2πx) sin(ax)Σ_(n=0) ^∞ e^(−2πnx) dx =Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(2π+2πn)x) sin(ax) dx =_(2π(n+1)x =t) Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) sin(a(t/(2π(n+1))))(dt/(2π(n+1))) =(1/(2π)) Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/(n+1)) ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) sin(((at)/(2π(n+1))))dt we have ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) sin(((at)/(2π(n+1))))dt =Im(∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))t) dt) and ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))t) dt =[−(1/(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))) e^(−(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))t) ]_0 ^∞ =(1/(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))) =((2π(n+1))/(2π(n+1)+ai)) =((2π(n+1)(2π(n+1)−ai))/(4π^2 (n+1)^2 +a^2 )) ⇒ Im(∫_0 ^∞ (....)dt) =((−2πa(n+1))/(4π^2 (n+1)^2 +a^2 )) ⇒ I =(1/(2π))Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/((n+1)))×((−2πa(n+1))/(4π^2 (n+1)^2 +a^2 )) =−a Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/(4π^2 (n+1)^2 +a^2 )) and this serie can be found by fourier ....](Q99427.png)
Commented by maths mind last updated on 20/Jun/20
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 20/Jun/20

| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 99413 by maths mind last updated on 20/Jun/20 | ||
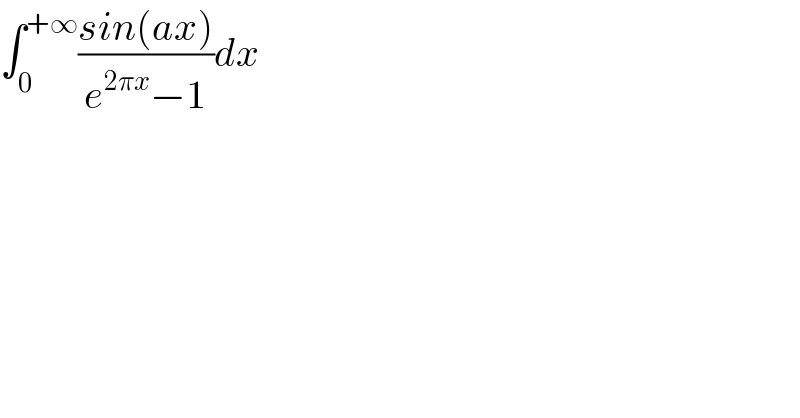 | ||
Answered by mathmax by abdo last updated on 20/Jun/20 | ||
![I =∫_0 ^∞ ((sin(ax))/(e^(2πx) −1))dx ⇒I = ∫_0 ^∞ ((e^(−2πx) sin(ax))/(1−e^(−2πx) )) =∫_0 ^∞ e^(−2πx) sin(ax)Σ_(n=0) ^∞ e^(−2πnx) dx =Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(2π+2πn)x) sin(ax) dx =_(2π(n+1)x =t) Σ_(n=0) ^∞ ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) sin(a(t/(2π(n+1))))(dt/(2π(n+1))) =(1/(2π)) Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/(n+1)) ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) sin(((at)/(2π(n+1))))dt we have ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) sin(((at)/(2π(n+1))))dt =Im(∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))t) dt) and ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))t) dt =[−(1/(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))) e^(−(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))t) ]_0 ^∞ =(1/(1+((ai)/(2π(n+1))))) =((2π(n+1))/(2π(n+1)+ai)) =((2π(n+1)(2π(n+1)−ai))/(4π^2 (n+1)^2 +a^2 )) ⇒ Im(∫_0 ^∞ (....)dt) =((−2πa(n+1))/(4π^2 (n+1)^2 +a^2 )) ⇒ I =(1/(2π))Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/((n+1)))×((−2πa(n+1))/(4π^2 (n+1)^2 +a^2 )) =−a Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (1/(4π^2 (n+1)^2 +a^2 )) and this serie can be found by fourier ....](Q99427.png) | ||
| ||
Commented by maths mind last updated on 20/Jun/20 | ||
 | ||
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 20/Jun/20 | ||
 | ||