
Question and Answers Forum
OthersQuestion and Answers: Page 127





Pg 122 Pg 123 Pg 124 Pg 125 Pg 126 Pg 127 Pg 128 Pg 129 Pg 130 Pg 131
|
Question and Answers Forum |
OthersQuestion and Answers: Page 127 |
| A uniform rod of AB of mass m=1.12 kg and lengtj l=100cm is placed on a sharp support O such that AO=a=40cm. To keep the rod horizontal, its end A is ties with a thread. Calculate reaction of support O on the rod when the thread is burnt. (g=10 m∙s^(−2) ) |
| Two cylindrical hollow drums of radii R and 2R, and of a common height h, are rotating with angular velocities ω (anti-clockwise) and ω (clockwise), respectively. Their axes, fixed are parallel and in a horizontal plane separated by (3R + δ). They are now brought in contact (δ → 0). (a) Show the frictional forces just after contact. (b) Identify forces and torques external to the system just after contact. (c) What would be the ratio of final angular velocities when friction ceases? |
| For a reversible reaction A ⇌ B. Find K_(eq) at 2727°C temperature. Given : Δ_r H° = −30 kJ mol^(−1) (at 2727°C) Δ_r S° = 10 JK^(−1) (at 2727°C) R = 8.314 JK^(−1) mol^(−1) |
| Figure shows two discs of same mass m. They are rigidly attached to a spring of stiffness k. The system is in equilibrium. From this equilibrium position, the upper disc is pressed down slowly by a distance x and released. Find the minimum value of x, if the lower disc is just lifted off the ground. |
| Two particle move along an x−axis. The position of particle 1 is given; by x=6.00t^2 +3.00t+2.00((m/s)) the acceleration of particle 2 is given by a=−8.00t((m/s^2 )) and,at t=0,its velocity is 20 ((m/s)).when the velocities of the particles match, what is their velocity? plzz help |
| Two blocks are moving together under the action of a constant horizontal external force F. If the smaller block is at rest with respect to the bigger block due to the friction between them, then the normal reaction between the bigger block and floor is |

|
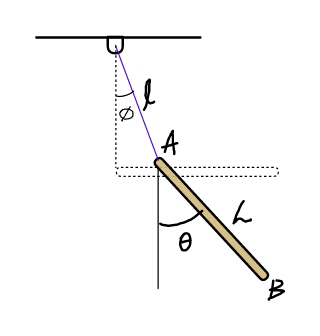
| In the figure shown below, all surfaces are smooth, strings and pulley are ideal. If the wedge is moving with acceleration a towards the right, then the acceleration of the block with respect to the wedge at that instant is |
| Find the centre of mass of a uniform (a) half-disc, (b) quarter-disc. |
| In a fuel cell, methanol is used as a fuel and O_2 is used as oxidizer. The standard enthalpy of combustion of methanol is −726 kJ mol^(−1) . The standard free energies of formation of CH_3 OH(l), CO_2 (g) and H_2 O(l) are −166.3, −394.4 and −237.1 kJ mol^(−1) respectively. The standard internal energy change of the cell reaction will be |
| The reversible expansion of an ideal gas under adiabatic and isothermal conditions is shown in the figure. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct? (1) T_1 = T_2 (2) T_3 > T_1 (3) w_(isothermal) > w_(adiabatic) (3) ΔU_(isothermal) > ΔU_(adiabatic) |
| Which of the following reaction is/are exothermic reaction/s? (1) CaCO_3 → CaO + CO_2 (2) Fe + S → FeS (3) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H_2 O (4) CH_4 + O_2 → CO_2 + 2H_2 O. |
| (n − 1) equal point masses each of mass m are placed at the vertices of a regular n-polygon. The vacant vertex has a position vector a with respect to the centre of the polygon. Find the position vector of centre of mass. |

|
| A plank of mass M kg is sliding on the smooth horizontal surface with constant velocity of 10 ms^(−1) . A another block of mass M kg is gently placed on it. The coefficient of friction between the block and the upper surface of the plank is 0.2. Assuming that plank is long enough such that the block does not fall from it. The velocity-time graph of the block is [Take g = 10 m/s^2 ] |
| Five moles of an ideal gas expand isothermally and reversibly from a pressure of 10 atm to 2 atm at 300 K. What is the largest mass (approx) which can be lifted through a height of 1 m in this expansion? |
| A door is hinged at one end and is free to rotate about a vertical axis. Does its weight cause any torque about this axis? Give reason for your answer. |

|

|

|

|
| Compare the bond strength of S − O bond in SO_3 ^(−2) and SO_4 ^(−2) ion. |
| A hemispherical bowl of radius R = 0.1 m is rotating about its own axis (which is vertical) with an angular velocity ω. A particle of mass 10^(−2) kg on the frictionless inner surface of the bowl is also rotating with the same ω. The particle is at a height h from the bottom of the bowl. It is desired to measure g (acceleration due to gravity) using the set up by measuring h accurately. Assuming that R and ω are known precisely and that the least count in the measurement of h is 10^(−4) m, what is the minimum possible error Δg in the measured value of g? |
| Compounds with high heat of formation are less stable because (1) it is difficult to synthesize them (2) energy rich state leads to instability (3) high temperature is required to synthesize them (4) molecules of such compounds are distorted |
| A one kg ball rolling on a smooth horizontal surface at 20 m s^(−1) comes to the bottom of an inclined plane making an angle of 30° with the horizontal. Calculate K.E. of the ball when it is at the bottom of incline. How far up the incline will the ball roll? Neglect friction. |

|
Pg 122 Pg 123 Pg 124 Pg 125 Pg 126 Pg 127 Pg 128 Pg 129 Pg 130 Pg 131 |