
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 181858 by KINMATICS last updated on 01/Dec/22

Answered by hmr last updated on 01/Dec/22
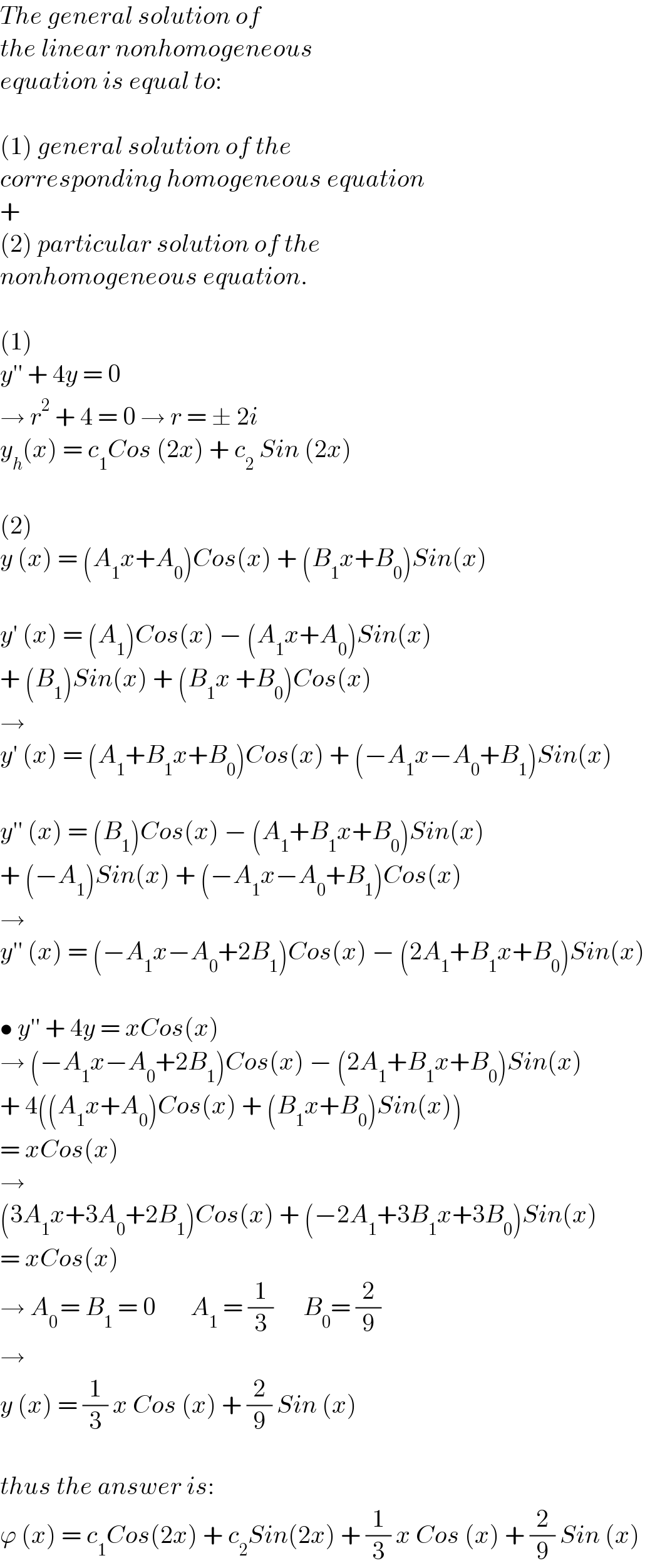
Commented by hmr last updated on 01/Dec/22
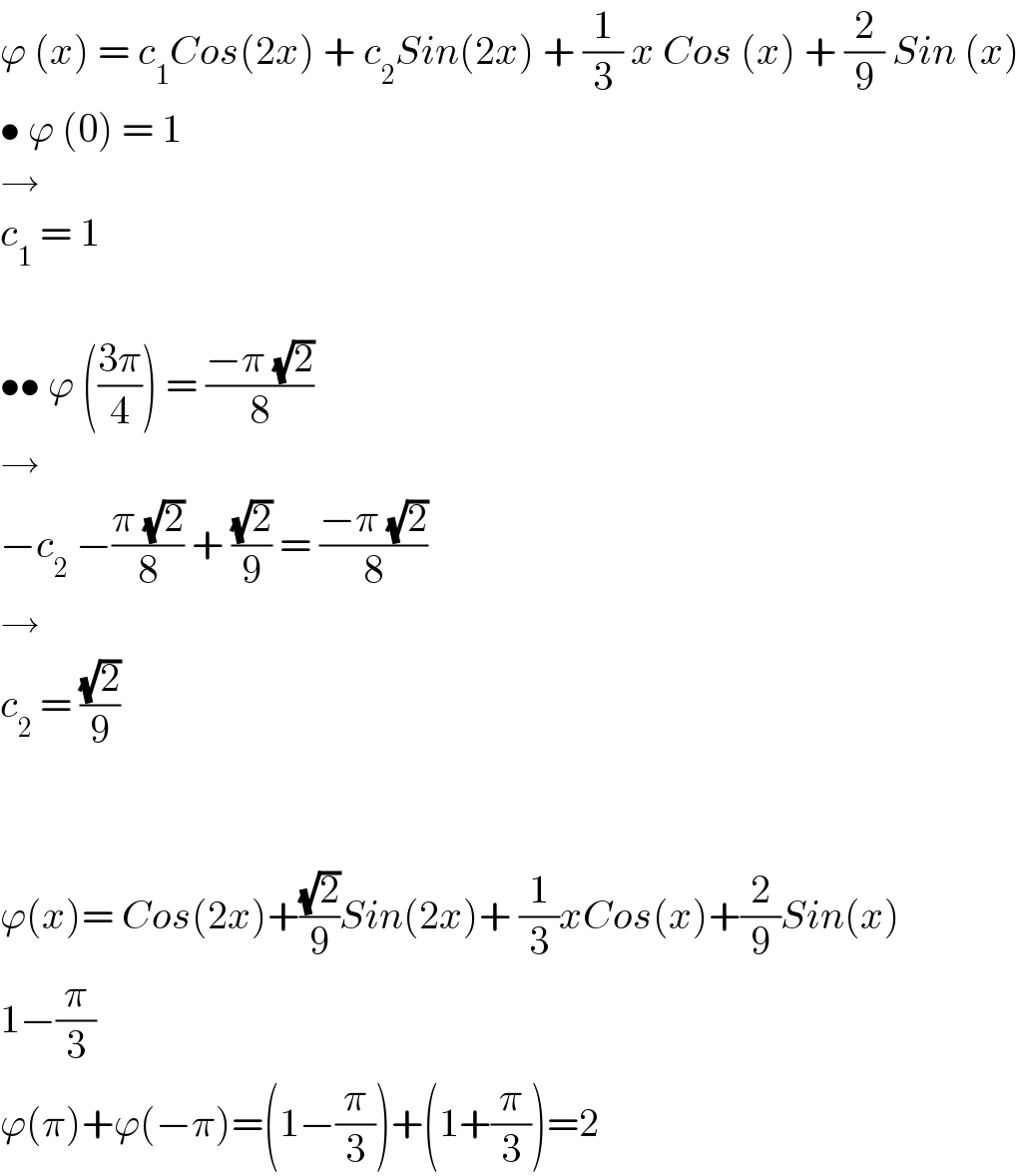
Answered by qaz last updated on 01/Dec/22

