
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 38373 by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 24/Jun/18

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 25/Jun/18
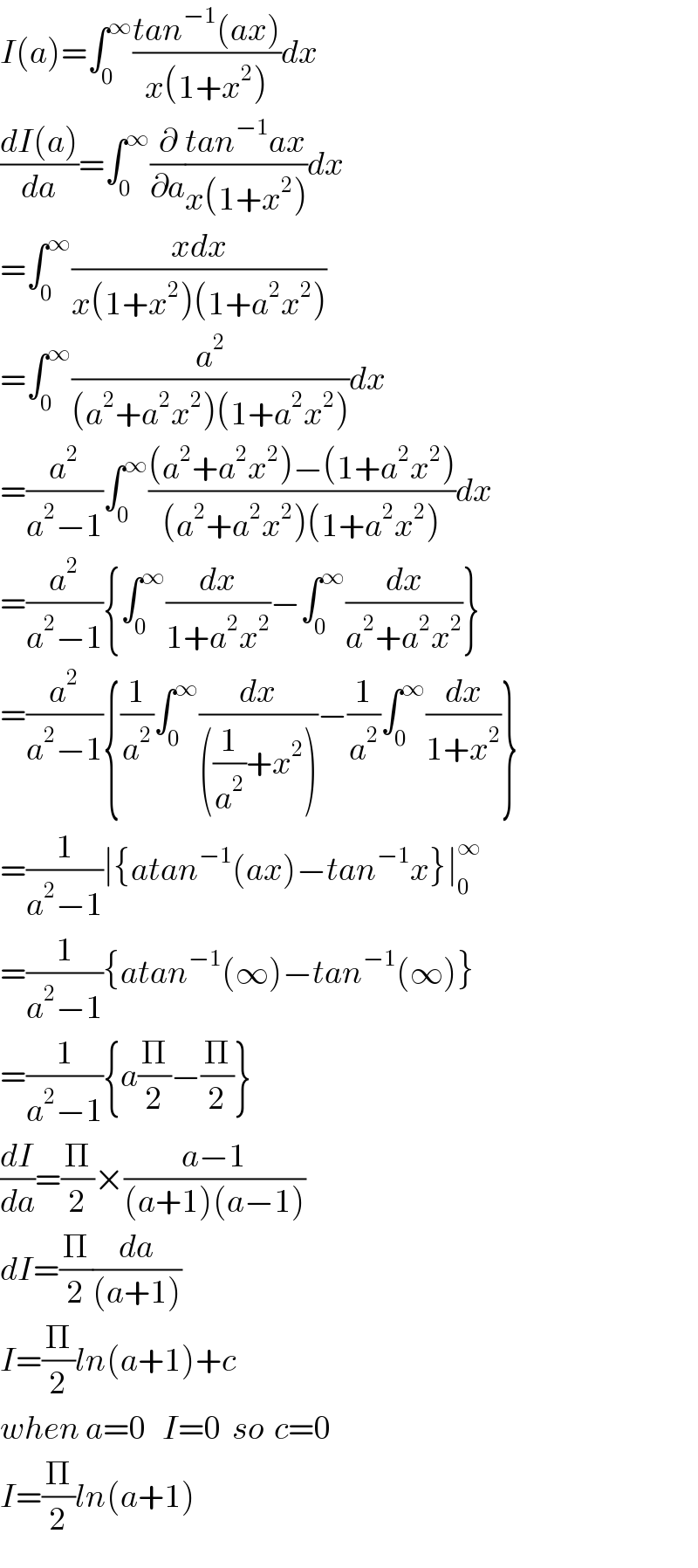
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 25/Jun/18

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 25/Jun/18

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 25/Jun/18

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 25/Jun/18

Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 25/Jun/18

Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 25/Jun/18

Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 25/Jun/18

