
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 73397 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 11/Nov/19
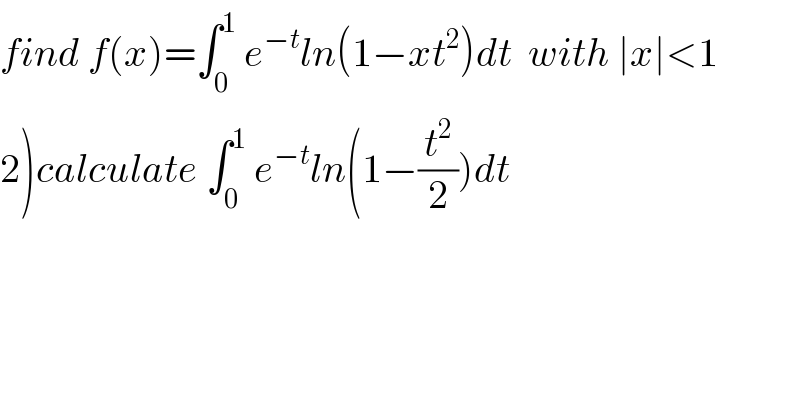
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 12/Nov/19
![1) we have ln^′ (1−u)=((−1)/(1−u)) =−Σ_(n=0) ^∞ u^n if ∣u∣<1 ⇒ ln(1−u) =−Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (u^(n+1) /(n+1)) +c (c=0) ⇒ ln(1−u) =−Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (u^n /n) we have ∣xt^2 ∣<1 ⇒ ln(1−xt^2 ) =−Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((x^n t^(2n) )/n) ⇒ f(x)=−∫_0 ^1 e^(−t) (Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((x^n t^(2n) )/n))dt =−Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (x^n /n) ∫_0 ^1 t^(2n) e^(−t) dt =−Σ_(n=1) ^∞ A_n (x^n /n) with A_n =∫_0 ^1 t^(2n) e^(−t) dt let determinate I_n =∫_0 ^1 t^n e^(−t) dt by parts u=t^n and v^′ =e^(−t) ⇒ I_n =[−e^(−t) t^n ]_0 ^1 +∫_0 ^1 nt^(n−1) e^(−t) dt =−e^(−1) +n I_(n−1) =nI_(n−1) −(1/e) (n>0) let W_n =(I_n /(n!)) ⇒W_(n+1) =(I_(n+1) /((n+1)!)) =(((n+1)I_n −(1/e))/((n+1)!)) =(I_n /(n!)) −(1/(e(n+1)!)) =W_n −(1/(e(n+1)!)) ⇒ W_(n+1) −W_n =−(1/(e(n+1)!)) ⇒ Σ_(k=0) ^(n−1) (W_(k+1) −W_k ) =−(1/e)Σ_(k=0) ^(n−1) (1/((k+1)!)) ⇒W_n =W_0 −(1/e) Σ_(k=1) ^n (1/(k!)) we have W_0 =I_0 =∫_0 ^1 e^(−t) dt =[−e^(−t) ]_0 ^1 =1−e^(−1) ⇒W_n =1−e^(−1) −(1/e)Σ_(k=1) ^n (1/(k!)) ⇒ I_n =n!W_n =n!{1−e^(−1) −e^(−1) Σ_(k=1) ^n (1/(k!))} ⇒ A_n =(2n)!{1−e^(−1) −e^(−1) Σ_(k=1) ^(2n) (1/(k!))} ⇒ f(x)=−Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (2n)!{1−e^(−1) −e^(−1) Σ_(k=1) ^(2n) (1/(k!))}(x^n /n) =(e^(−1) −1)Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (((2n)!)/n) x^n +e^(−1) Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (((2n)!)/n)(Σ_(k=1) ^(2n) (1/(k!)))x^n .....be continued....](Q73469.png)
Answered by mind is power last updated on 11/Nov/19
![f(x)=[−e^(−t) ln(1−xt^2 )]_0 ^1 +∫_0 ^1 ((e^(−t) .−2xt)/(1−xt^2 ))dt =−e^(−1) ln(1−x)−2x∫_0 ^1 .((te^(−t) dt)/((1−(√x)t)(1+(√x)t))) =−e^(−1) ln(1−x)−(√x)∫_0 ^1 ((e^(−t) .(1+t(√x)−(1−t(√x))))/((1−t(√x))(1+t(√x))))dt =−e^(−1) ln(1−x)−(√x)∫_0 ^1 ((e^(−t) dt)/(1−t(√x)))+(√x)∫_0 ^1 ((e^(−t) dt)/(1+t(√x))) let u=1−t(√x) in first and s=1+t(√x) in 2nd =−e^(−1) ln(1−x)+∫_1 ^(1−(√x)) (e^((u−1)/(√x)) /u)du+∫_1 ^(1+(√x)) (e^((1−s)/(√x)) /s)ds m=(u/(√x)) in first m=(s/(√x)) in]2nd =−e^(−1) ln(1−x)+∫^((1/(√x))−1) _(1/(√x)) ((e^m .e^(−(1/(√x))) )/m).dm+∫_(1/(√x)) ^(1+(1/(√x))) e^(1/(√x)) .e^(−m) .(dm/m)346 We use Ei(w)=∫_(−∞) ^w (e^x /x)dx=∫_∞ ^(−w) (e^(−x) /x)dx Ei is exponential integral function we get −e^(−1) ln(1−x)+{Ei((1/(√x))−1)−Ei((1/(√x)))}e^((−1)/(√x)) +e^(1/(√x)) {Ei(−1−(1/(√x)))−Ei(−(1/(√x)))} ∫_0 ^1 e^(−t) ln(1−(t^2 /2))dt put x=(1/2) =e^(−1) ln(2)+{Ei((1/(√2))−1)−Ei((1/(√2)))}e^(−(1/(√2))) +e^(1/(√2)) {Ei(−1−(1/(√2)))−Ei((1/(√2)))}](Q73414.png)
Commented by mind is power last updated on 11/Nov/19

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 11/Nov/19

