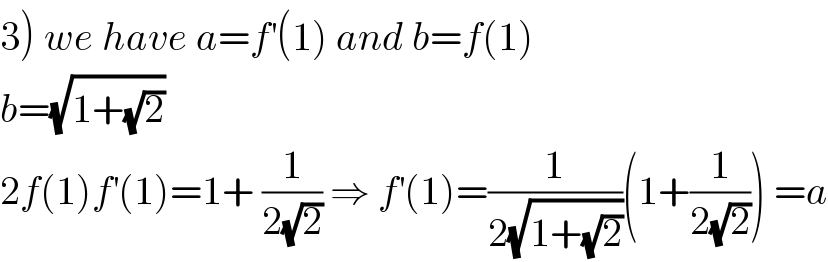Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 37892 by abdo mathsup 649 cc last updated on 19/Jun/18

Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 21/Jun/18

Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 21/Jun/18
![1) x ∈ D_f ⇔ x+1≥0 and x+(√(x+1))≥0 ⇒ x ≥−1 and x +(√(x+1))≥0 so if x ≥0 we get x+(√(x+1)) >0 if −1≤x≤0 (√(x+1)) +x =(√(x+1)) −(−x) and ((√(x+1)))^2 −(−x)^2 =x+1 −x^2 =−x^2 +x +1 ⇒Δ=1−4(−1)=5 x_1 =((−1+(√5))/2) andx_2 = ((−1−(√5))/2) (√(x+1)) +x = ((x+1 −x^2 )/((√(x+1))−x)) and (√(x+1)) −x>0 so (√(1+x))+x ≥0 ⇔ x ∈[((−1−(√5))/2) , ((−1+(√5))/2)] but [−1,0]⊂[((−1−(√5))/2),((−1+(√5))/2)] ⇒D_f =[−1,+∞[ 2) y =f^′ (0)x +f(0) but f(x)=(√(x+(√(x+1)))) ⇒ f(0)=1 we have f^2 (x)=x +(√(x+1)) ⇒ 2f(x)f^′ (x)=1+ (1/(2(√(x+1)))) ⇒2f(0)f^′ (0)= (3/2) ⇒ f^′ (0) =(3/4) so the equation of assymptote is y= (3/4) x+1 .](Q38077.png)
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 21/Jun/18